Agile Methodology Basics
Intro
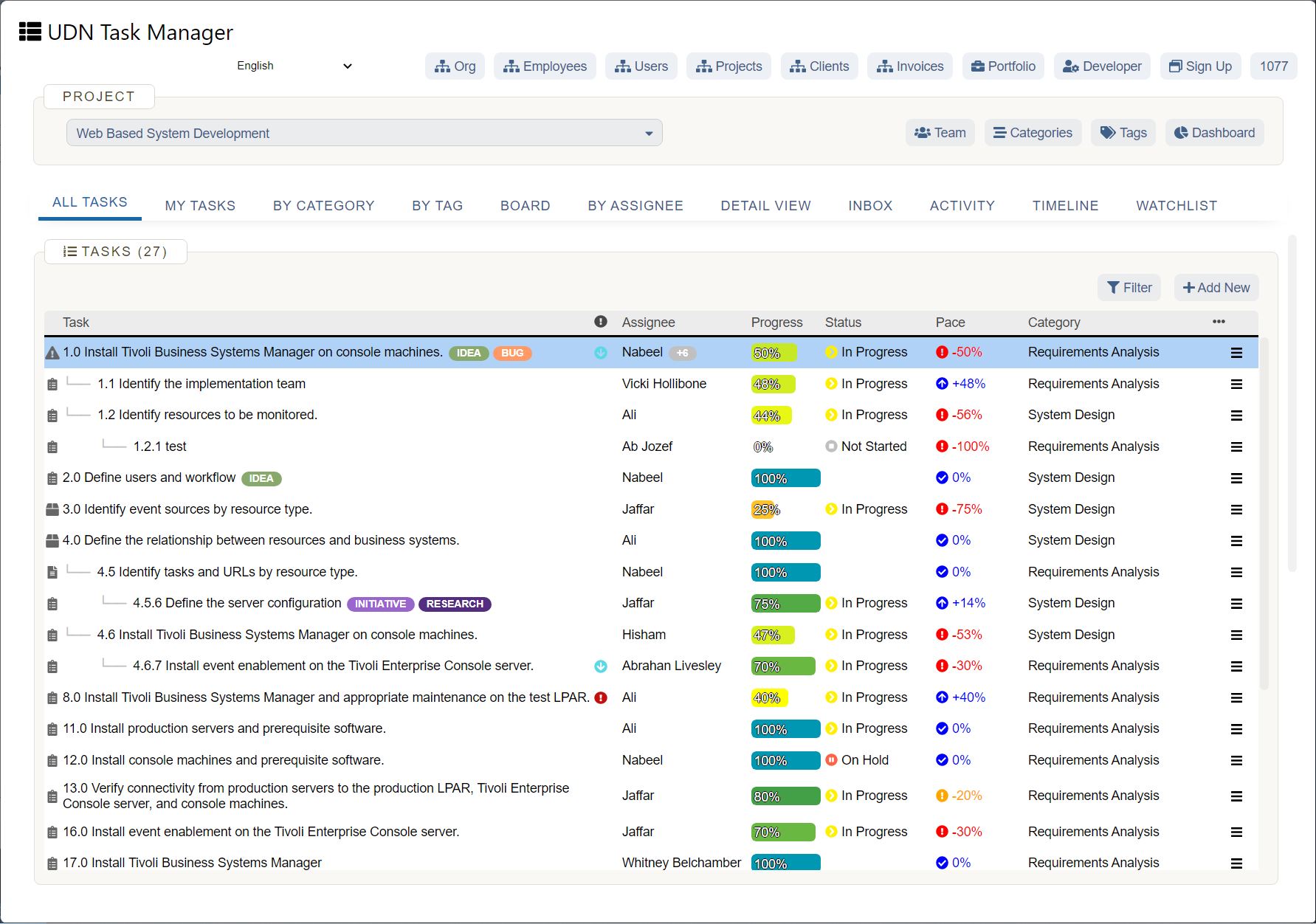
Agile is a project management approach developed as a more flexible and efficient way to get products to market. The word ‘agile’ refers to the ability to move quickly and easily. Therefore, an Agile approach enables project teams to adapt faster and easier compared to other project methodologies.
Many of today’s projects have more unknowns than a traditional project management methodology can adequately handle. This uncertainty makes it challenging to document requirements and adapt to changes successfully.
This guide will explain the Agile methodology, which projects will benefit from an Agile approach, and how to implement one effectively.
What is Agile methodology?
Agile methodology is an approach to project management that uses four values and 12 principles to organize projects.
The four values of the Agile Manifesto are:
The Agile method works in ongoing sprints of project planning and execution, enabling you to continuously adapt and mature your plan, scope, and design throughout the project.
Agile projects require an iterative approach, which supports incremental, frequent, and consistent delivery of workable products to your customer or client. This innovative approach ensures your project team can consistently deliver concrete products without being delayed by changes and evolving requirements.
Agile has a high level of customer involvement and includes frequent reviews of progress with both the project team and the customer.
You can run an Agile project using several different frameworks. Some of the more popular ones include:
This video on the Agile methodology further explains the approach, breaking down everything from the core principles to the Agile frameworks.
The history of Agile methodology
Depending on the source, the origins of Agile methodology can be traced back to the 1990s , 1975 , or even as early as the 1960s . However, everyone agrees that Agile took root with the creation of the Manifesto for Agile Software Development , also known as The Agile Manifesto.
The Agile Manifesto was originally released in February 2001 to create a new way of managing software development. A group of leading software developers wrote the manifesto on a retreat in Utah, where they had met to discuss industry problems and potential solutions.
This group understood that the software industry needed a better, quicker way to get products to market. Their goal was to develop new methods for changing a product and project that would not impact the cost or delay the production schedule.
They determined that dividing a project into shorter iterations would allow for faster development and testing. Reviews (called sprint retrospectives) would take place at the end of every iteration, and changes could then be made without having to wait for the end product.
The Agile Manifesto was initially drafted as a solution for software development management, but the Agile methodology has since grown to encompass projects across various industries and businesses.
The 12 Agile principles
The Manifesto for Agile Software Development outlines 12 Agile principles that all projects should follow. These are:
The benefits of Agile project management
The benefits of Agile project management are many, particularly for the following organizations and project types:
Traditional project management methods generally only had the project team in touch with the customer at the start and end of the project. If customer requirements or expectations were not captured correctly in the beginning or changed over time, the project team had no idea until it was too late. With Agile, there’s ongoing contact throughout the entire process and iterative deliveries to ensure your team is on track, so the end product will be exactly what the customer wants.
What if your customer told you halfway through a project that they needed a scope change? Using a traditional approach to project management, this either couldn’t be accommodated or likely involved significant increases to both the project cost and schedule. With Agile, you can incorporate changes with minimal effort, no matter how far along in the project.
Agile incorporates a continuous development approach that ensures your team is continuously delivering workable products. Instead of waiting for six to 12 months or longer for an end product, your client is getting a working version of the product at much shorter intervals, typically every two to four weeks.
Your team is developing versions of the product regularly and getting customer feedback early on, minimizing the risk of a project failing. Breaking a large project into iterations reduces your risk of an iteration or draft failure. You’re more likely to find small problems early that can be addressed quickly, rather than discovering a large issue only at the time of final testing before the end delivery. If later you encounter a problem or need to cancel the project, you’ll have invested less time and money.
Agile supports collaboration and continuous improvement, both of which can lead to innovation and the development of new products and features. Co-locating teams and having daily meetings encourages brainstorming and idea creation. Agile supports an “ idea meritocracy ” where the best idea wins out, no matter who it comes from. The project team, other stakeholders, and the customer can figure out functionality and features together.
When not to use the Agile project management method
Despite the many benefits of Agile, the methodology is not for every project or organization. But how do you know when not to use the Agile project management method? What are the advantages and disadvantages of Agile methodology?
Agile is intended to help reduce the cost of change and uncertainty on a project by breaking it down into iterative project management stages. However, if there’s already very little uncertainty and a low possibility of change, Agile may not be the most effective approach. For instance, if you work in an industry with heavy regulations or where many of the project requirements are already known, you don’t need iterative planning and multiple drafts.
By definition, a project is “a temporary endeavor with a beginning and an end, and it must be used to create a unique product, service or result .” But what if a customer asks you to construct five identical houses, and you decide to create a separate project and team for each one? Using Agile could result in five unique houses rather than five identical ones. One of the disadvantages of Agile is that it’s not designed for reproducibility.
An Agile project requires continuous contact with your stakeholders. However, some may not have the time, ability, or desire to dedicate themselves to a project. If the project is considered low value or low risk, they may prefer a more traditional approach where you only involve them at key phases or final delivery.
If your company or project team isn’t ready, adopting the Agile development cycle can introduce risk to your project.
Here are five indicators that your company isn’t ready to use Agile :
Agile vs. Scrum
The Agile method outlines the best practices for organizing projects based on the four values and 12 Agile software development principles documented in the Agile Manifesto. You may have seen comparisons between Scrum and Agile. The definition of Scrum is “a framework for project management that emphasizes teamwork, accountability, and iterative progress toward a well-defined goal.” Scrum is a framework that you can use to implement these Agile principles, values, and best practices.
To better understand Agile vs. Scrum, you can think of Scrum as a guideline for adopting the Agile approach to project management. Scrum provides the rules, roles, events, tools, and artifacts necessary for successfully adopting an Agile mindset.
The main difference between Agile and Scrum is that Agile is the process you want to achieve, and Scrum is a tool for its success. You will often hear Scrum and Agile used interchangeably, as Scrum is the most popular framework for Agile. However, it’s not the only framework you can implement to plan and run an Agile project.
Agile vs. Waterfall project management

Agile methodology project management and Waterfall project management are two of the more popular methods for organizing projects. When determining how to plan and run your next project, you’ll likely start by comparing Agile and Waterfall project management to determine which is more suitable.
Waterfall is a more traditional approach to project management, involving a linear project flow. It’s best for clearly defined projects with definitive timelines and well-defined deliverables from the outset. In other words, if your major project constraints are well understood and documented, Waterfall is likely your best option.
The core principles of Waterfall include:
Conversely, Agile was created to handle projects where the primary constraints are not well understood.
As discussed earlier, Agile is an iterative, flexible approach to projects. This method splits a project into stages or “sprints,” allowing it to mature and evolve as you gain more information.
When deciding between Waterfall project management and Agile, it should ultimately come down to your end product’s maturity and how well you understand the project’s outcomes and requirements in the initiation phase.
Additional Agile resources
Here are some Agile resources that delve further into the Agile methodology and how to successfully implement it:











