What Is Business Forecasting? Why It Matters
Companies conduct business forecasts to determine their goals, targets, and project plans for each new period, whether quarterly, annually, or even 2–5 year planning .
Forecasting helps managers guide strategy and make informed decisions about critical business operations such as sales, expenses, revenue, and resource allocation . When done right, forecasting adds a competitive advantage and can be the difference between successful and unsuccessful companies.
In this guide to business forecasting, we'll cover:
An introduction to business forecasting
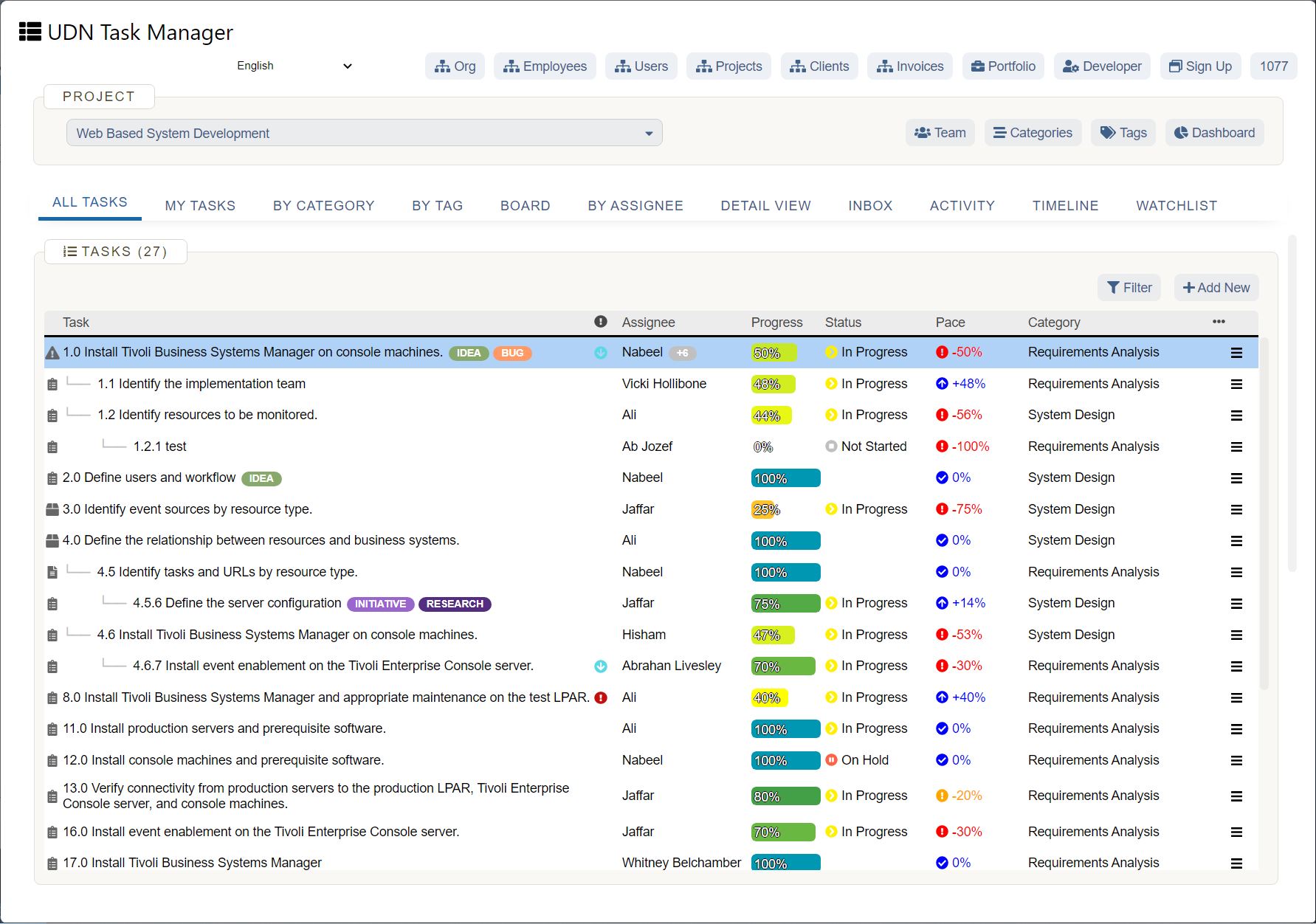
What is business forecasting? Business forecasting is a projection of future developments of a business or industry based on trends and patterns of past and present data.
This business practice helps determine how to allocate resources and plan strategically for upcoming projects, activities, and costs. Forecasting enables organizations to manage resources , align their goals with present trends, and increase their chances of surviving and staying competitive.
The purpose of forecasts is to develop better strategies and project plans using available, relevant data from the past and present to secure your business's future . Good business forecasting allows organizations to gain unique, proprietary insights into likely future events, leverage their resources, set product team OKR, and become market leaders.
Managers conduct careful and detailed business forecasts to guarantee sound decision-making based on data and logic, not emotions or gut feelings.
What are important business forecasting methods?
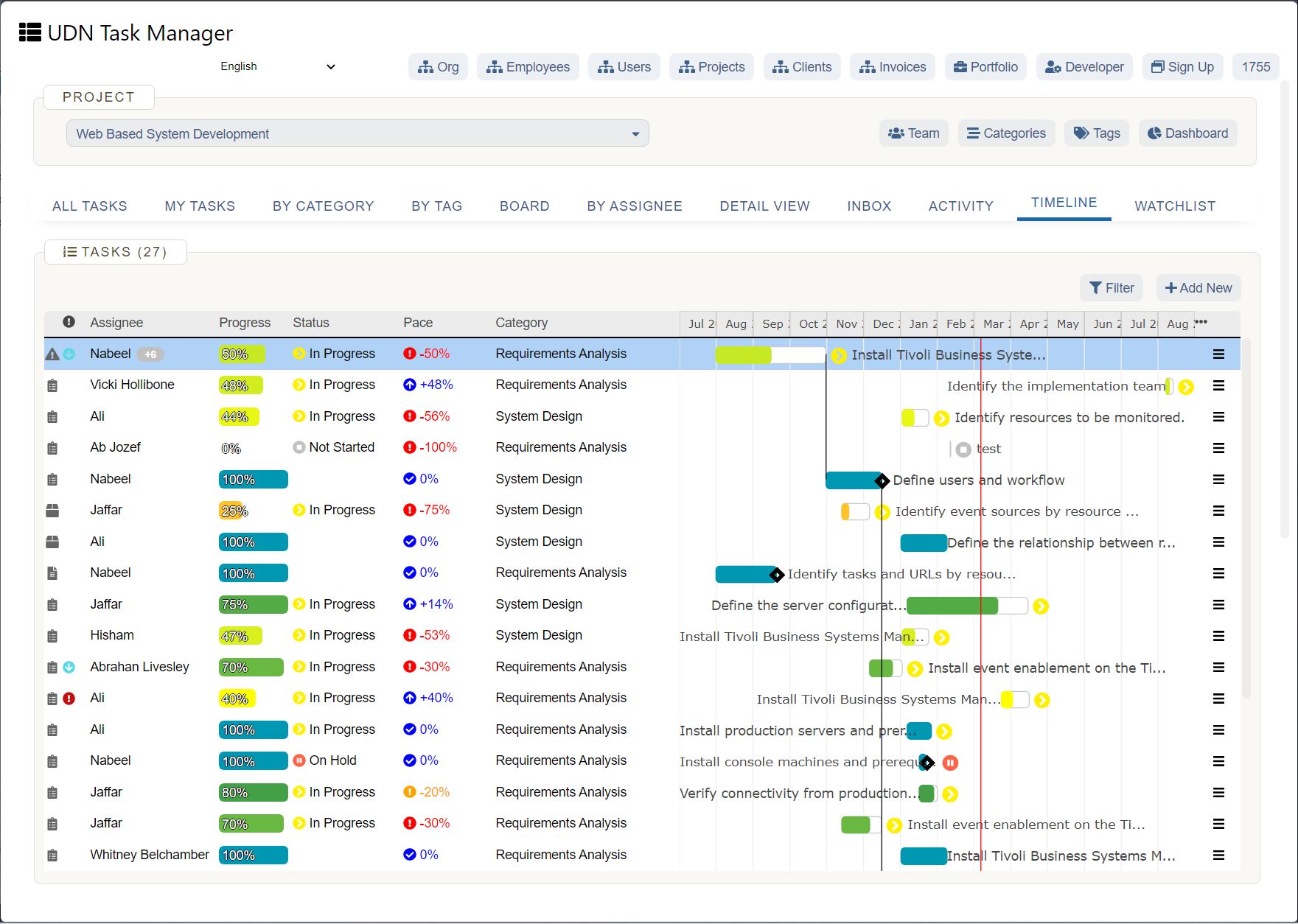
There are several business forecasting methods. They fall into two main approaches:
Quantitative and qualitative forecasting techniques use and provide different sets of data and are needed at different stages of a product's life cycle.
Note that significant changes in a company, such as new product focus, new competitors or competitive strategies, or changing compliance requirements diminish the connection between past and future trends. This makes choosing the right forecasting method even more important.
Quantitative business forecasting
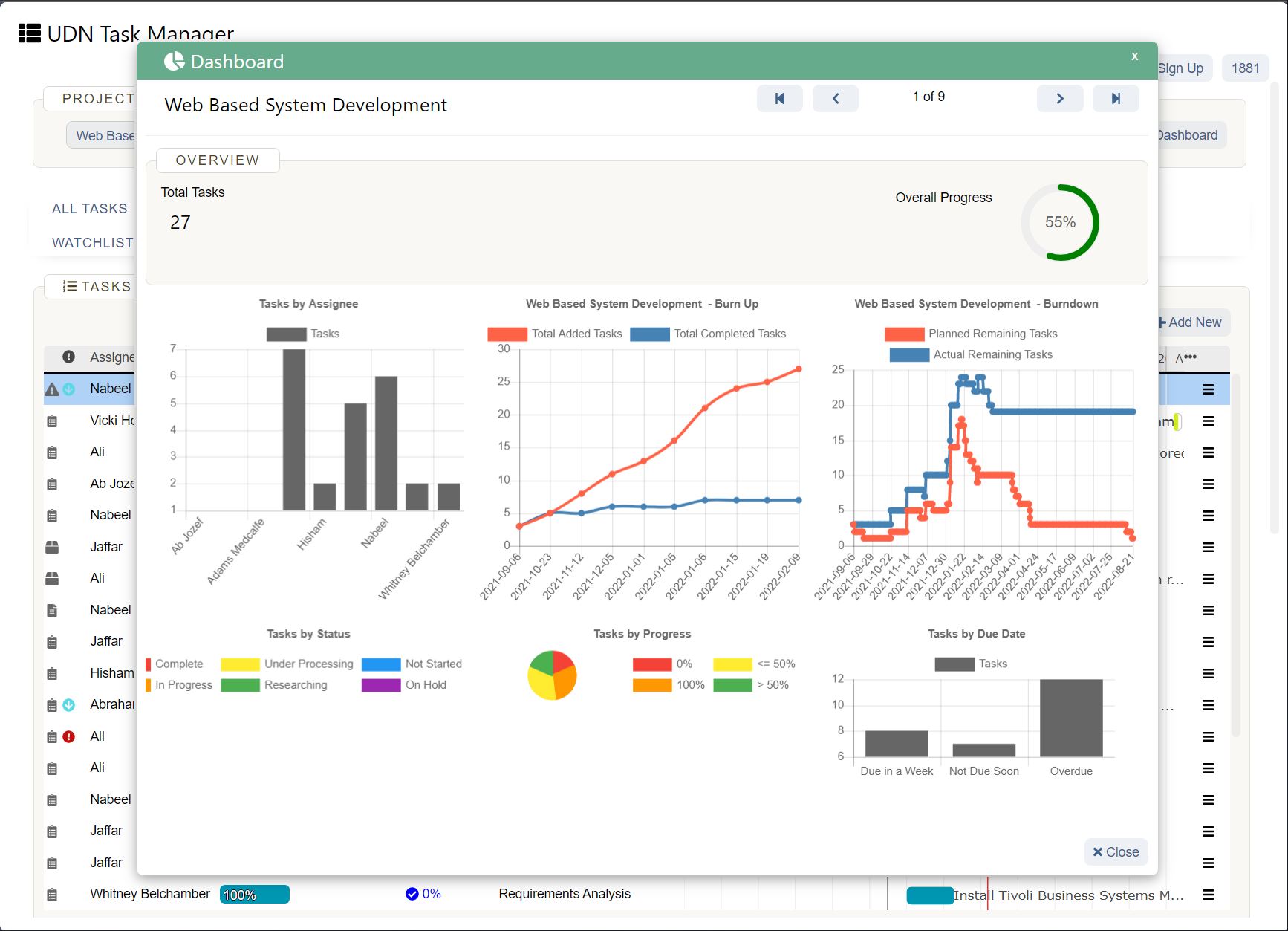
Use quantitative forecasting when there is accurate past data available to analyze patterns and predict the probability of future events in your business or industry.
Quantitative forecasting extracts trends from existing data to determine the more probable results. It connects and analyzes different variables to establish cause and effect between events, elements, and outcomes. An example of data used in quantitative forecasting is past sales numbers.
Quantitative models work with data, numbers, and formulas. There is little human interference in quantitative analysis. Examples of quantitative models in business forecasting include:
Qualitative forecasting
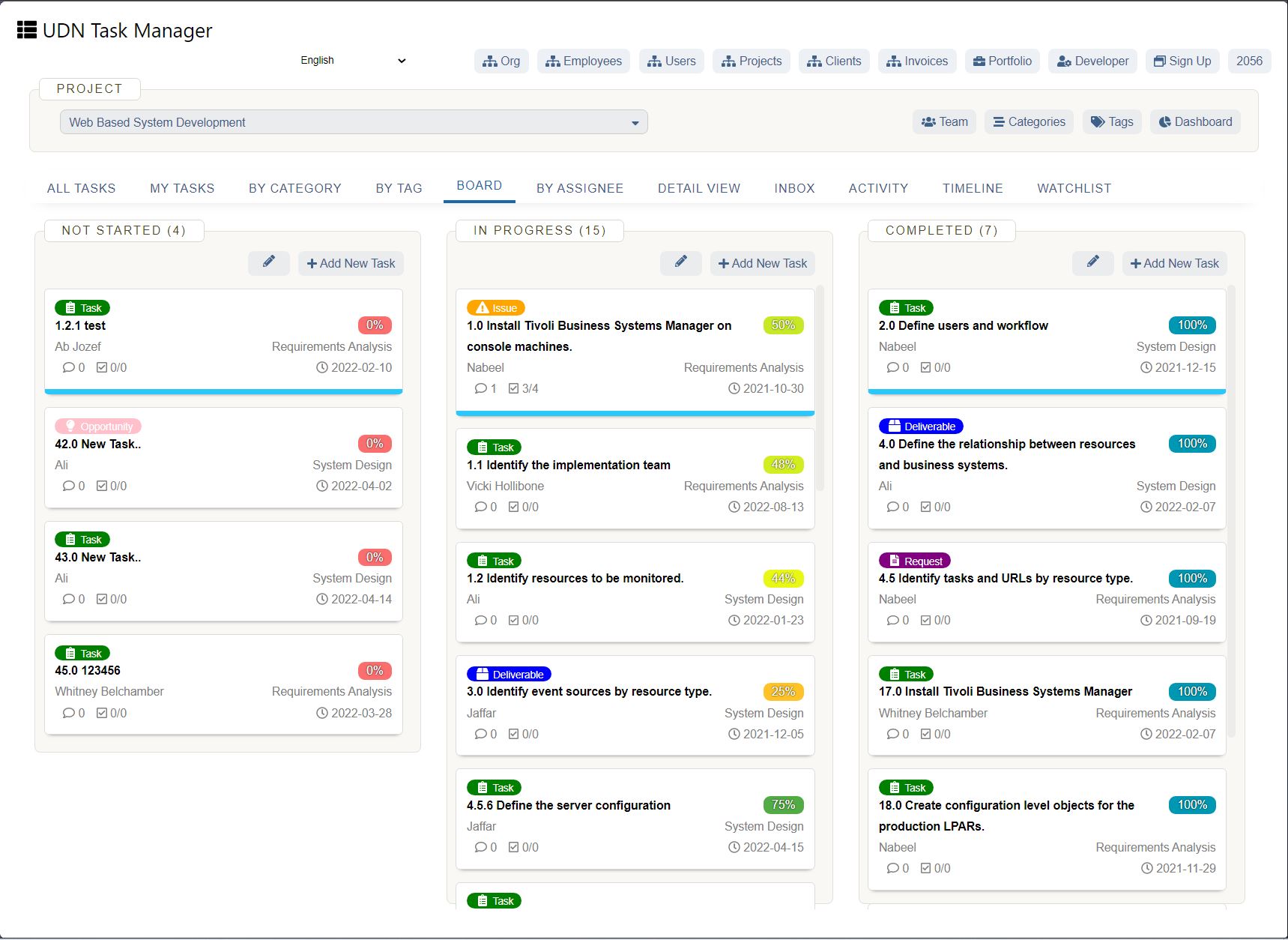
Qualitative business forecasting is predictions and projections based on experts' and customers' opinions. This method is best when there is insufficient past data to analyze to reach a quantitative forecast. In these cases, industry experts and forecasters piece together available data to make qualitative predictions.
Qualitative models are most successful with short-term projections. They are expert-driven, bringing up contrasting opinions and reliance on judgment over calculable data. Examples of qualitative models in business forecasting include:
How do you choose the right business forecasting technique?
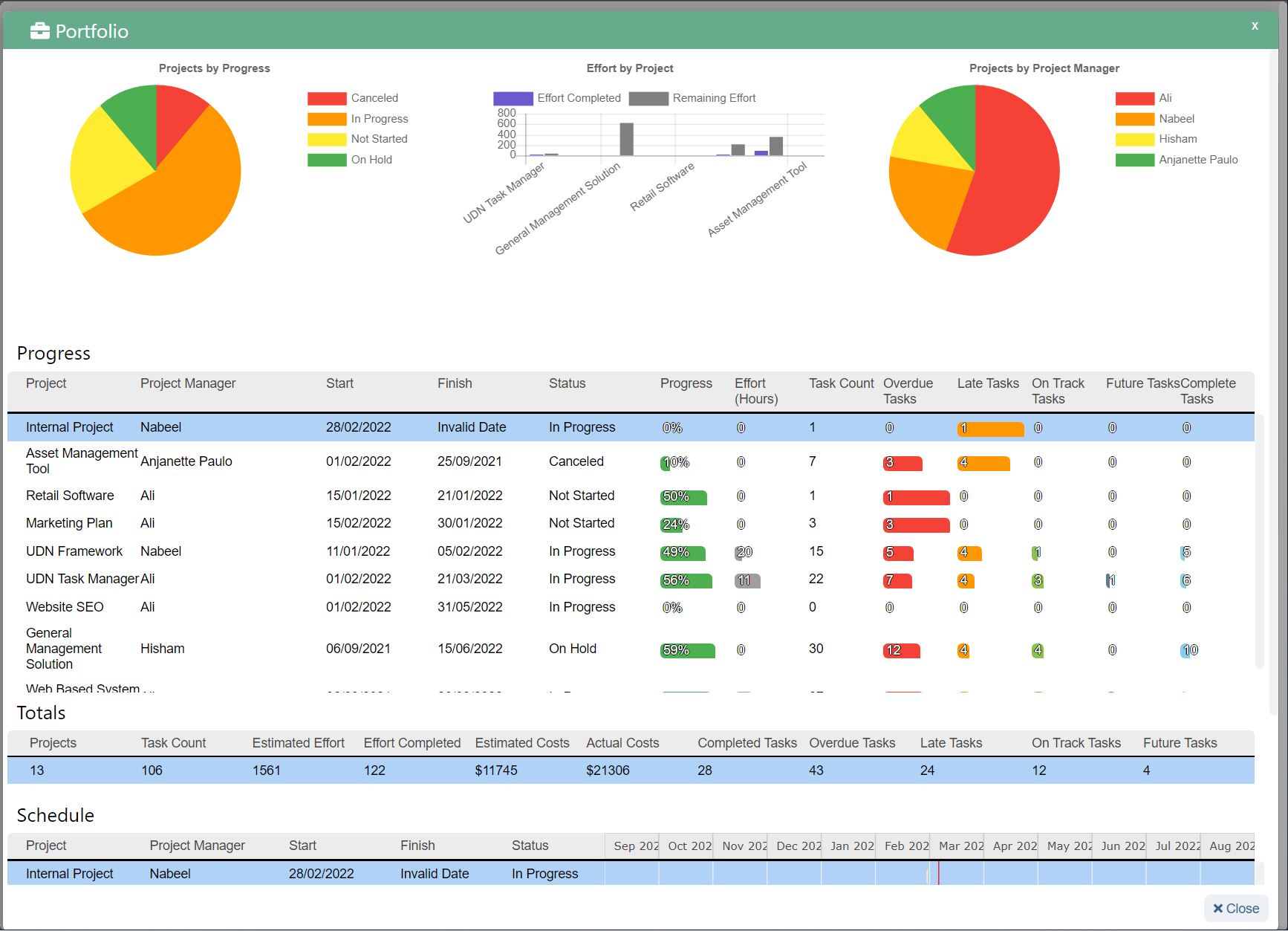
Managers and forecasters must consider the stage of the product or business as this influences the availability of data and how you establish relationships between variables. A new startup with no previous revenue data would be unable to use quantitative methods in its forecast.
The more you understand the use, capabilities, and impact of different forecasting techniques, the more likely you will succeed in business forecasting.
Why is business forecasting important?
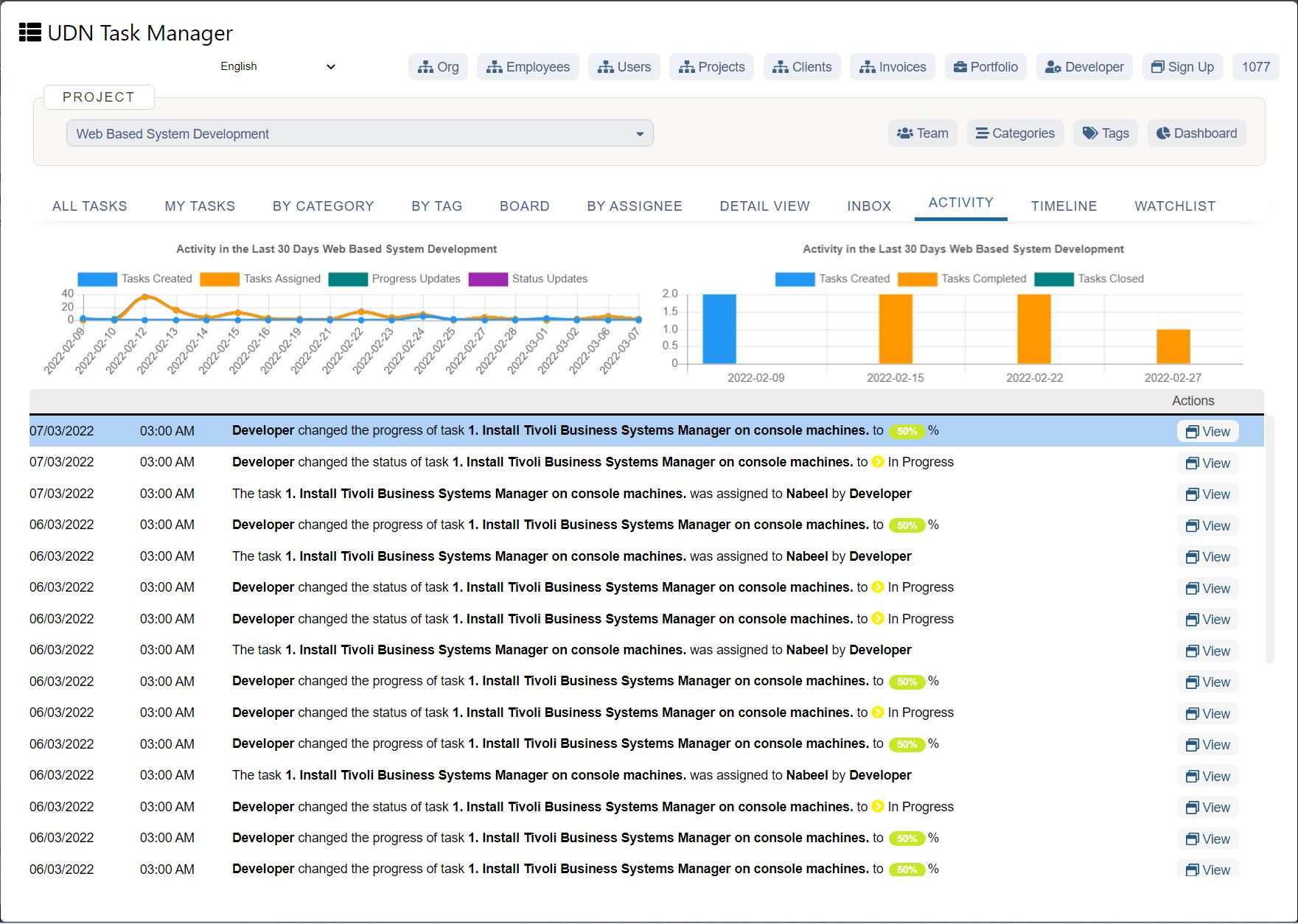
Any insight into the future puts your organization at an advantage. Forecasting helps you predict potential issues, make better decisions, and measure the impact of those decisions.
By combining quantitative and qualitative techniques, statistical and econometric models , and objectivity, forecasting becomes a formidable tool for your company.
Business forecasting helps managers develop the best strategies for current and future trends and events. Today, artificial intelligence, forecasting software, and big data make business forecasting easier, more accurate, and personalized to each organization.
Forecasting does not promise an accurate picture of the future or how your business will evolve, but it points in a direction informed by data, logic, and experiential reasoning.
What are the integral elements of business forecasting?
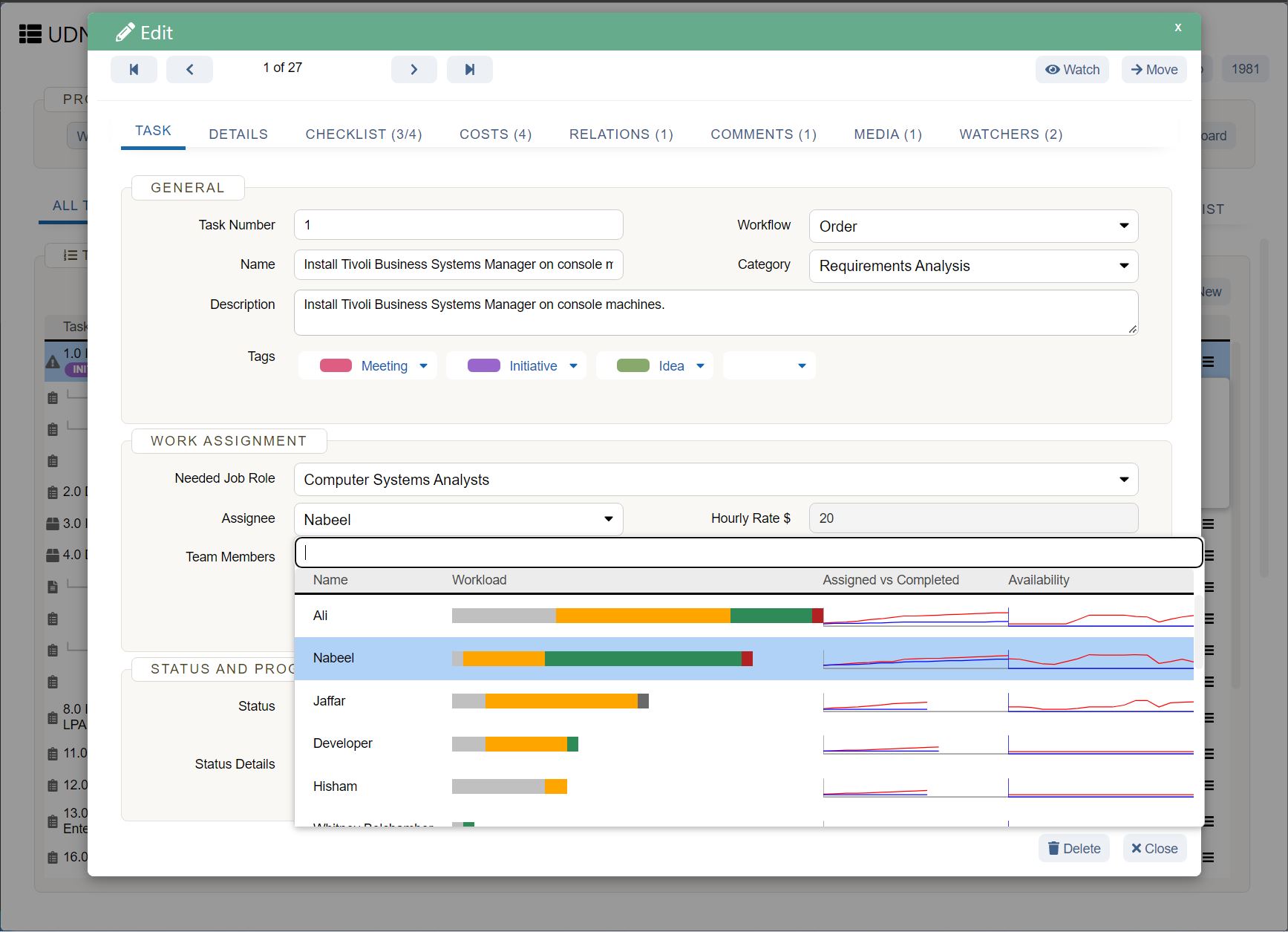
While there are different forecasting techniques and methods, all forecasts follow the same process on a conceptual level. Standard elements of business forecasting include:
How do you do business forecasting?

Successful business forecasting begins with a collaboration between the manager and forecaster. They work together to answer the following questions:
Once these answers are clear, choose the best forecasting methods based on the stage of the product or business life cycle, availability of past data, and skills of the forecasters and managers leading the project.
With the right forecasting method, you can develop your process using the integral elements of business forecasting mentioned above.
How do you get data for business forecasting?
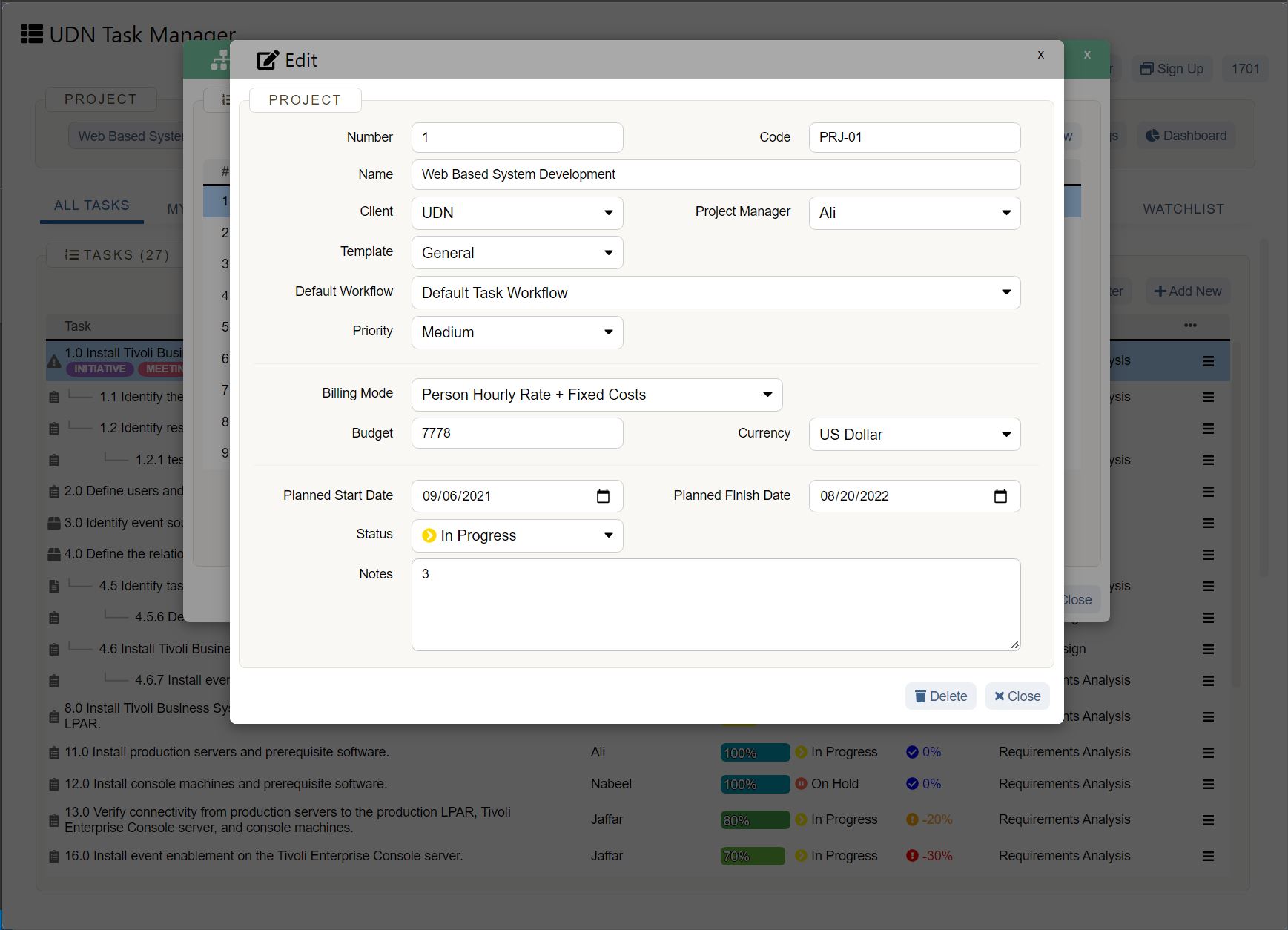
A forecast is only as good as the data supplied. Before collecting data, ask:
When you have these answers, you can start collecting data from two main sources:
Business forecasting examples
Some forecasting examples for business include:
What are the limits of business forecasting?
You can follow the rules, use the right methods, and still get your business forecast wrong. It is, after all, an attempt to predict the future. Some limits to business forecasting include:
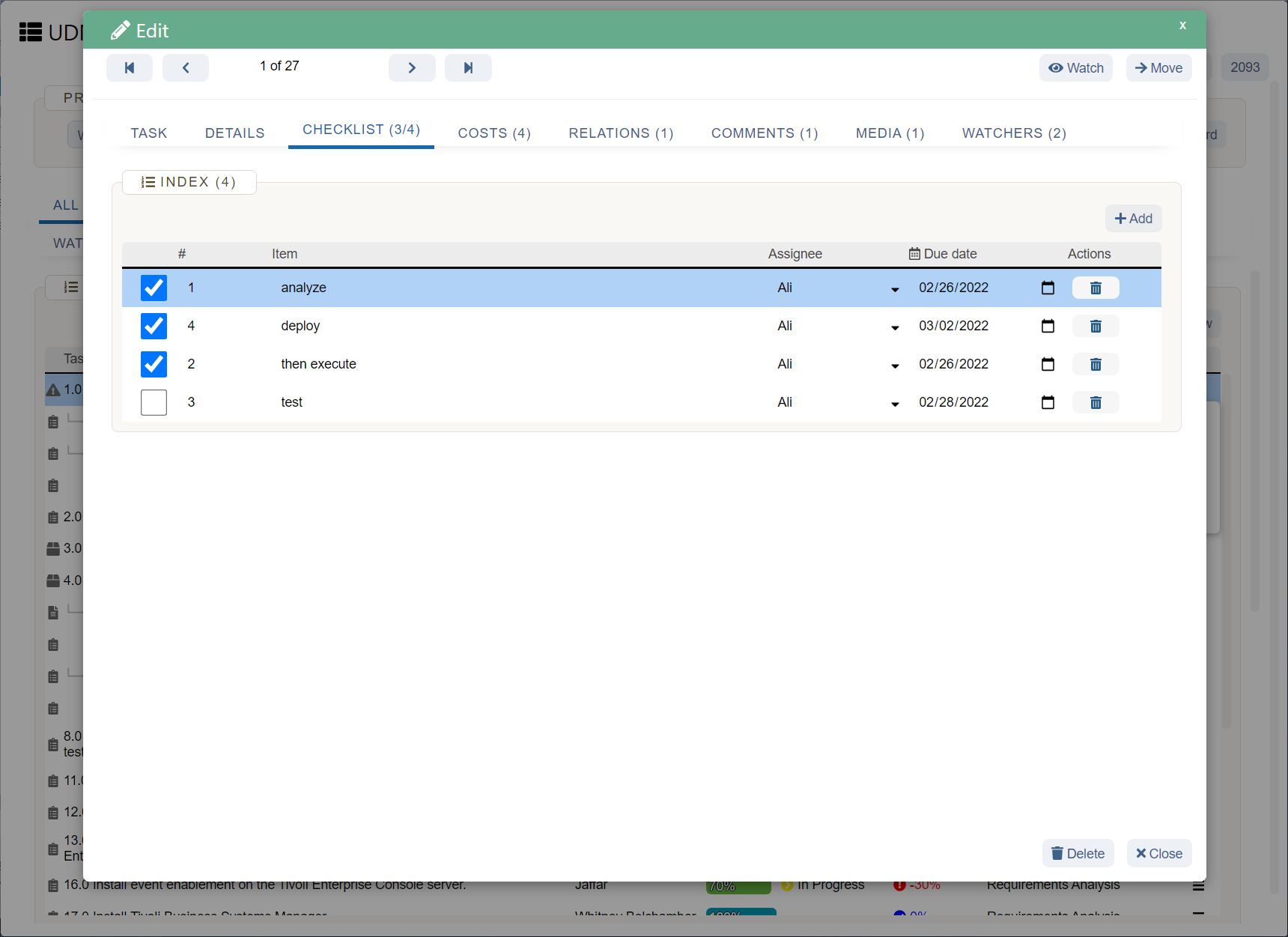
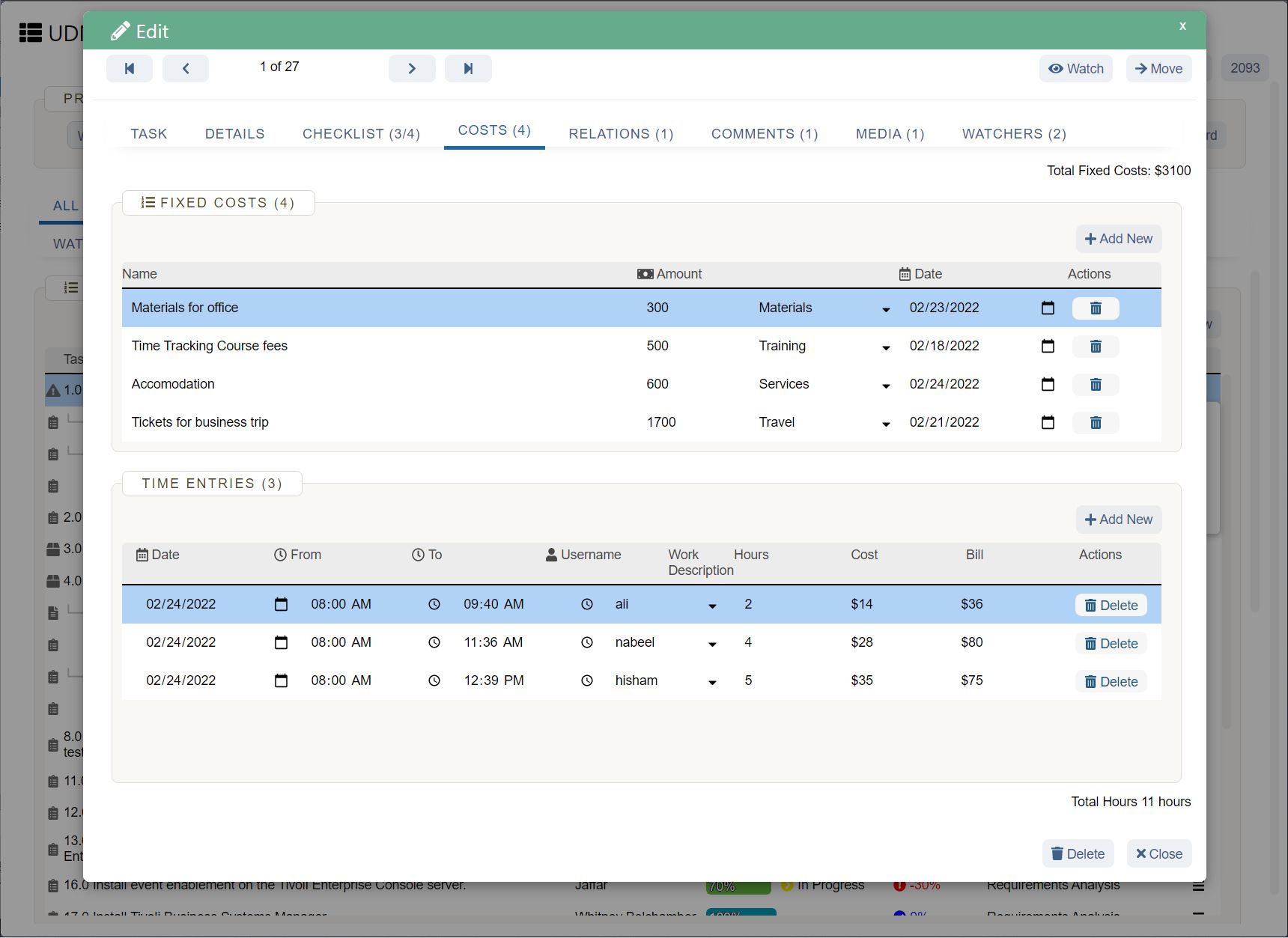
How UDN Task Manager helps with business forecasting
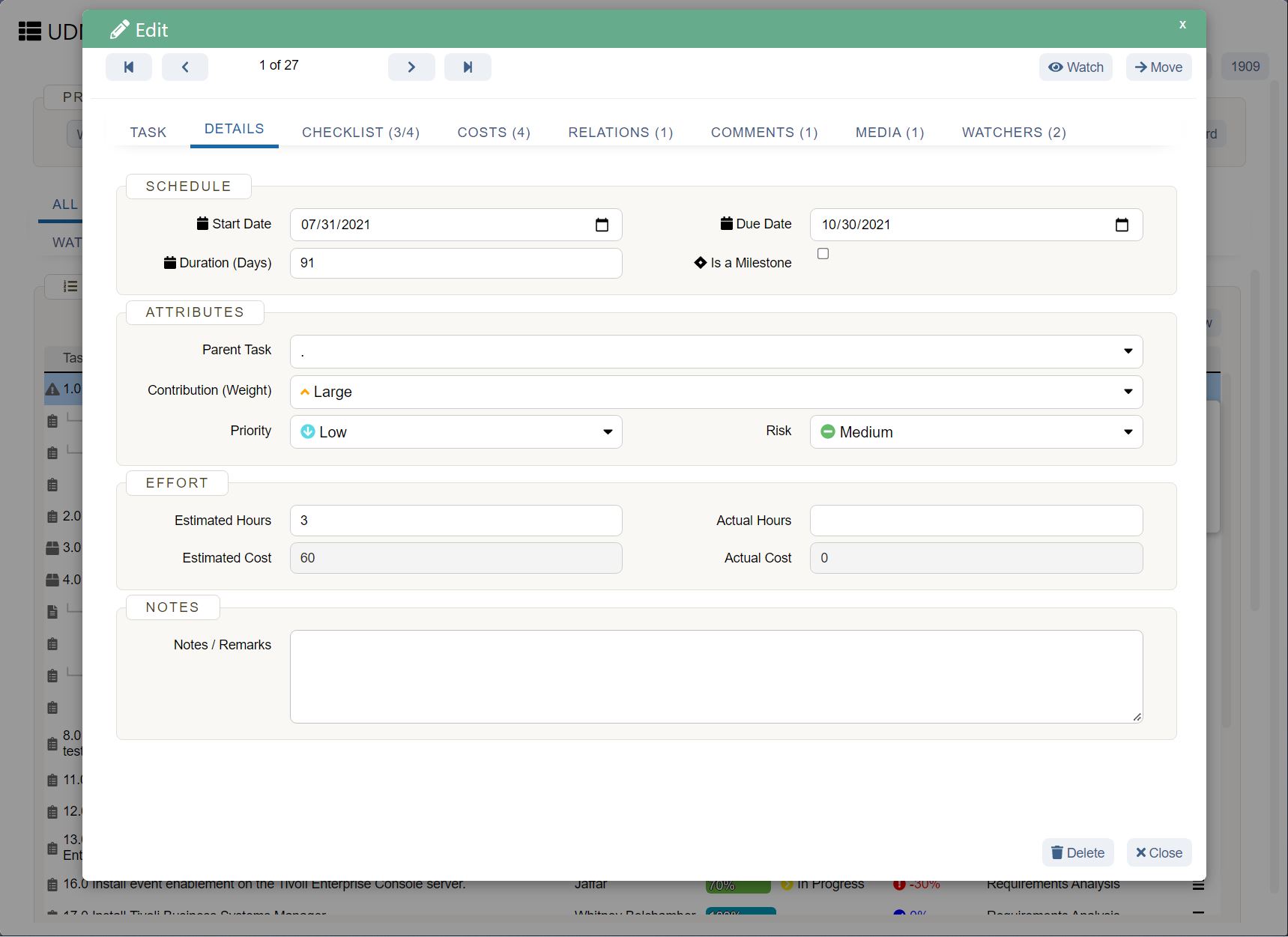
The more accurate your business forecasting, the more effective your strategies and plans can be. While many things in business are out of your control, having an informed forecast of what lies ahead makes you prepared and confident about the future.
UDN Task Manager helps gather data in one central platform, extract insights, and communicate findings with forecasters and managers. Other benefits of UDN Task Manager include real-time data, integrations with other forecasting software, streamlined collaboration, and visibility into every business forecasting project.
Are you ready to make projections for your business, allocate your resources for the best results, and improve your business forecasting process? Get started with a two-week free trial of UDN Task Manager today.











