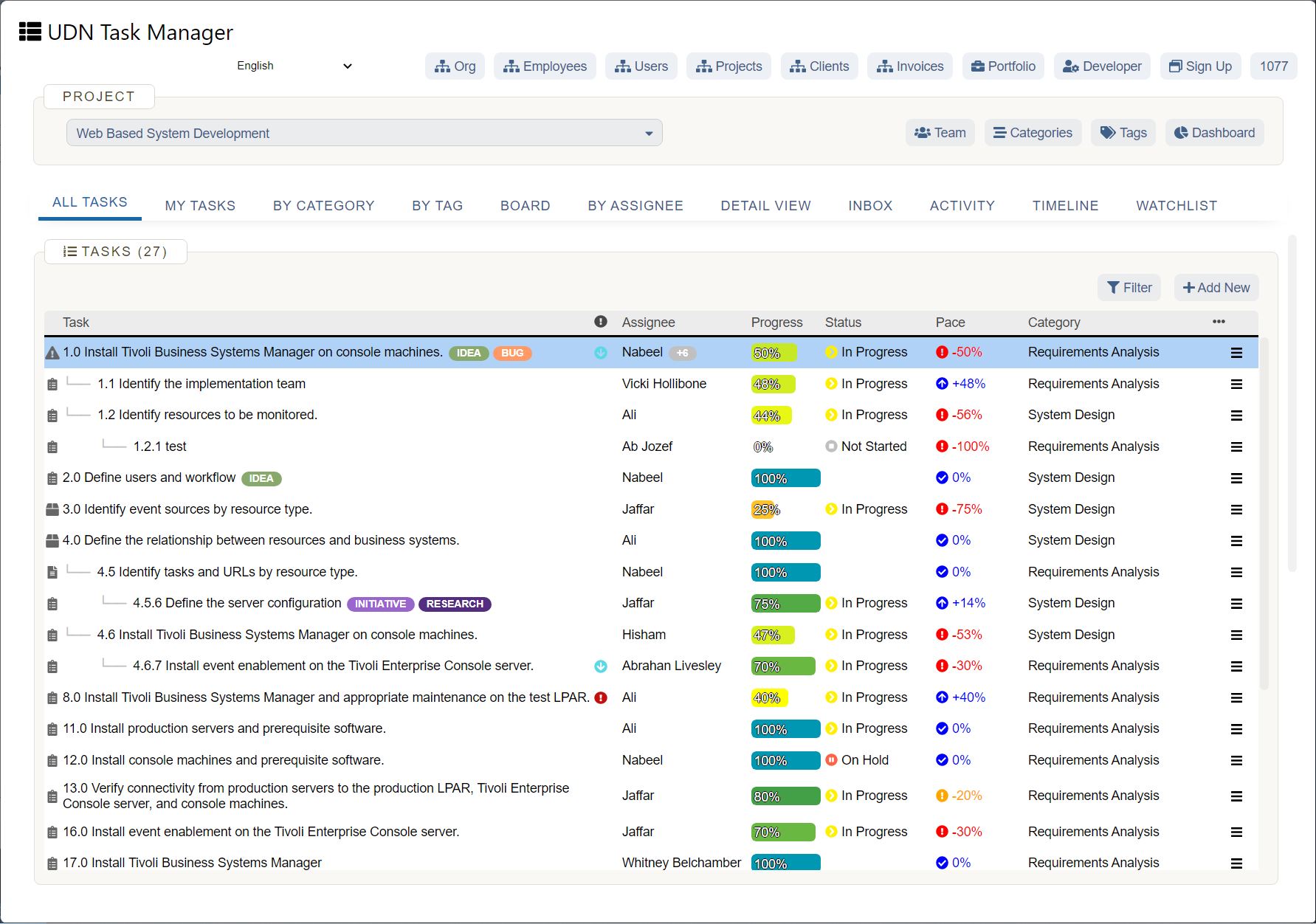
The Ultimate Guide to Capacity Planning
Project managers in professional services succeed when they are able to look ahead and plan based on the “big picture.” In the context of professional services, capacity planning is how firms can ensure they have the right resource capacity plan available to meet future client demand.
Capacity planning also helps organizations understand and prepare for future operating costs because it assesses variables beyond current resource levels.
What is capacity planning?
Capacity planning is how PMs and resource managers assess and address the future needs of their organization. It requires a strategic, long lens approach that takes into account things like future demand, past data, trends, seasonal changes, and even irregular conditions. Insights like these help PMs and resource managers make decisions based on actionable data.
Specifically referring to labor, capacity planning in business ensures the necessary amount of individuals with the appropriate skill sets are available to work on certain projects and initiatives.
Let’s say that a company plans to roll out a website redesign within the next six months. A resource manager would make sure the appropriate amount of copywriters, designers, and programmers are all available to work on the project so it is completed in time.
While it is fairly simple to envision capacity planning when it comes to physical production, information technology capacity planning is an increasingly important element for businesses in the digital services realm. As digital companies grow, they will need to ensure their IT capacity planning takes into account increased needs for memory, processing power, and storage space.
Will more staff need to be hired? Are there any skills that are lacking and need to be accounted for? Will staff need to work overtime or take on more than their current workload? Will freelancers or contractors be needed? Capacity planning can be a balancing act, so it may be useful to look at the resources utilized during similar projects. Past data will likely provide insights around timelines, labor, and costs.
Businesses rarely (if ever) set their budgets “on-the-fly” and capacity planning helps organizations gain a firm grasp on future operating costs months and sometimes years in advance.
Capacity planning can often be confused with resource planning. While both share a common goal of leveraging resources to meet organizational goals, capacity planning involves anticipating future resource needs, while resource planning involves the efficient management of resources to complete a task at hand.
Challenges of capacity planning
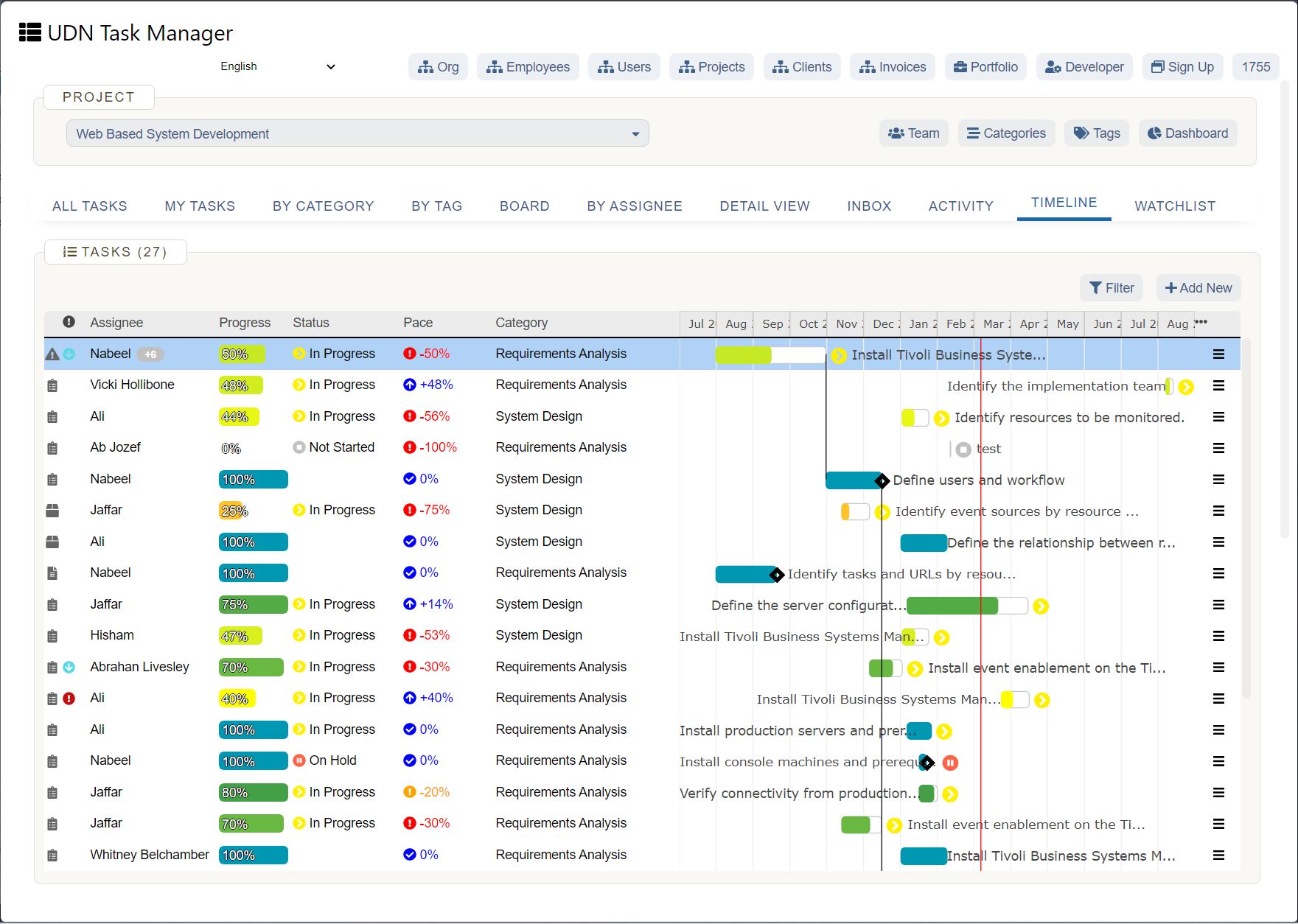
You may find there are some challenges and barriers associated with capacity planning . For instance, changes in leadership may make it difficult to predict what project or resource decisions should be made. One PM may lay out an ambitious approach to tackling the project portfolio, while another may take a more conservative approach. If future leadership is unclear, planning in this way may prove challenging.
Additionally, a lack of visibility into employee workload can be a roadblock to efficient capacity planning. Operating from a position of darkness makes it difficult to assess which resources are available for which projects, which resources are being over- or underutilized, and which resources you simply don’t have at your disposal.
Types of capacity planning
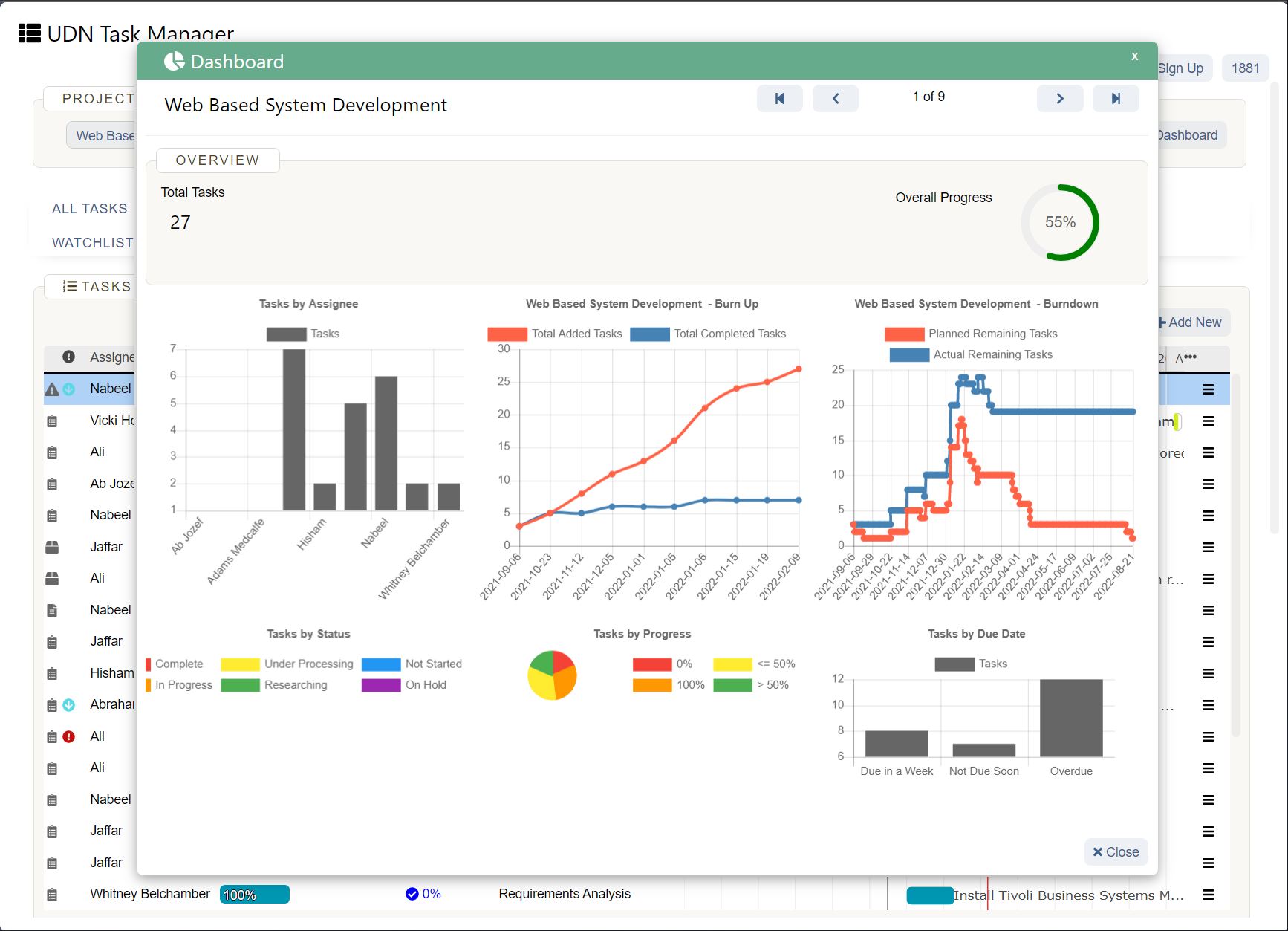
Because capacity planning is such a broad area, there are severely different types of capacity planning product managers can use to ensure they have the right amount of resources at a given time. The three types of capacity planning are product, workforce, and tool capacity planning.
Types of capacity planning strategies
In addition to types of capacity planning, there are actually several capacity planning strategies that can help ensure you have enough products to satisfy customer demand . Understanding what strategic capacity planning is will allow product managers to use the information they have to adjust production timelines, whether that is in advance of extra demand or in response to it.
Combined with the various types of capacity planning, these capacity planning strategies should help production managers plan, react, and respond to changes in demand, workforce, and tools over a period of time.
How to do capacity planning
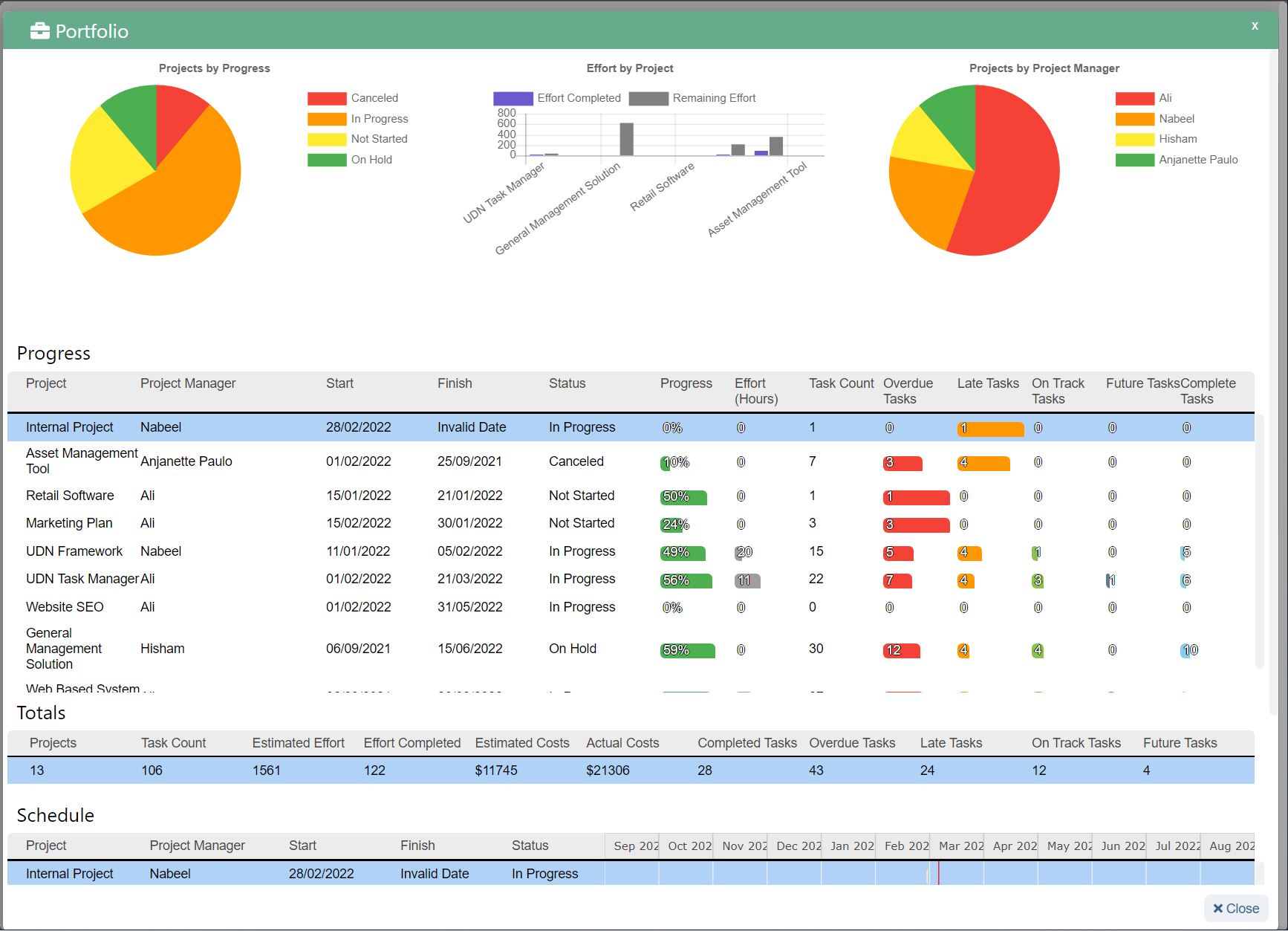
Capacity planning involves several key steps that ensure a product manager considers all the important elements that go into creating an accurate estimation of resources. The steps for capacity planning involve determining capacity requirements, analyzing current capacity, and planning for future demands.
The first step in any capacity planning process is to determine the capacity needed to meet basic demand. To figure out general capacity, you’ll look to the production plan or materials plan, which should give the correct indication of how much capacity will be needed to meet demand. In this first step, production managers should be able to determine workloads based on the resources required to meet production demands.
In the second step of capacity planning, product managers can compare the results of the first step with their actual production capacity. This requires looking at the current production schedule and analyzing the current production capacity by considering actual versus predicted output. Analyzing current capacity also allows product managers to make more accurate predictions about future capacity and identify opportunities for meeting increased demand in the future.
Planning for the future is the final step in capacity planning and involves creating a capacity plan that can help you anticipate bottlenecks and find the most optimal production schedule to efficiently meet demand. If, through the first two steps, you conclude that your company would not be able to meet an increase in demand in the future, now is the time to look at potential avenues to increase production, whether through increased shifts, additional machines, or streamlining production processes.
What is capacity management?
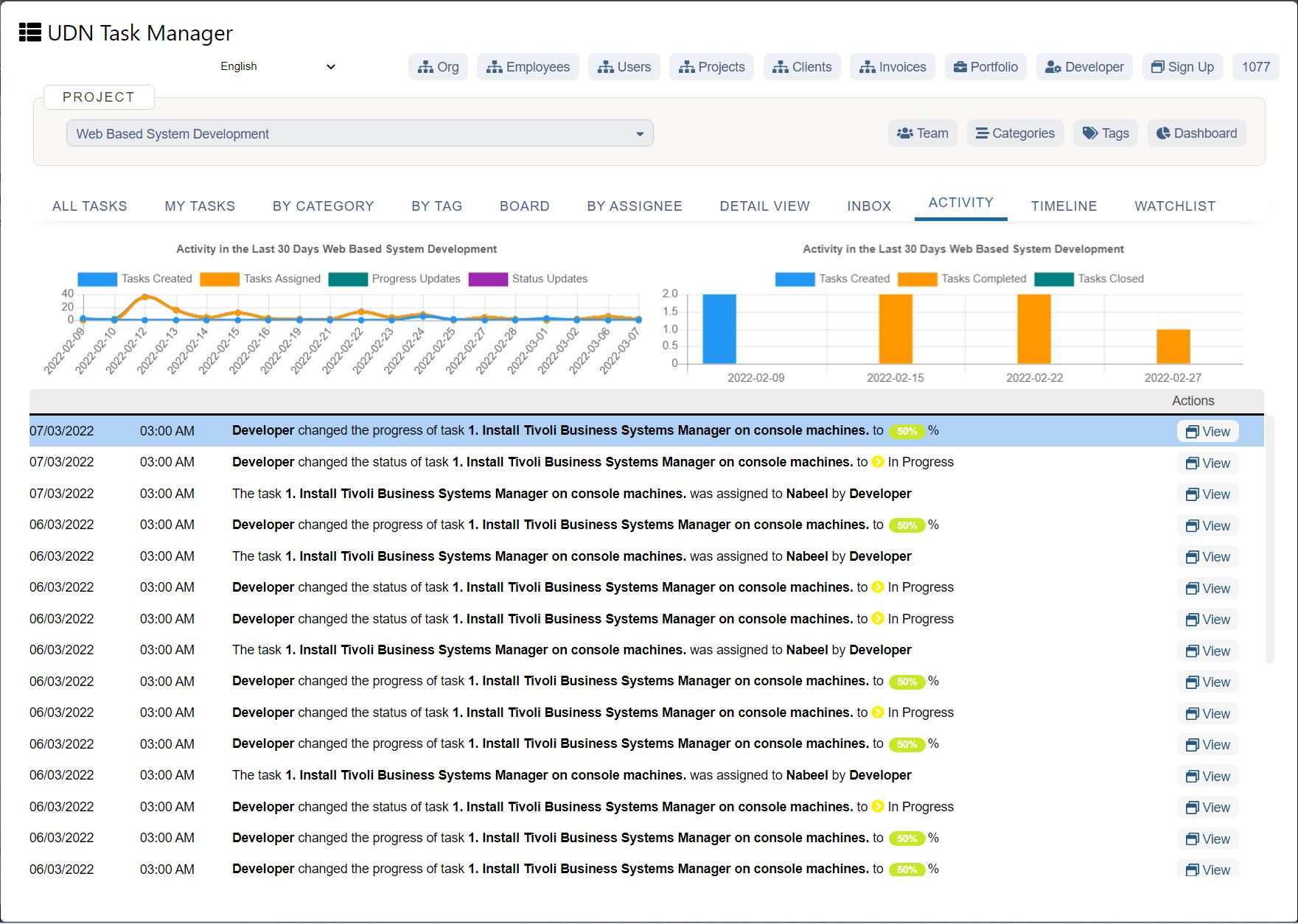
Capacity management takes capacity planning even further, focusing on helping a company maximize their capacity for production at all times and under all circumstances. Whereas capacity planning would typically be a job responsibility of a product manager or even a business owner, capacity management is often its own role. A capacity manager ensures a company has the resources and infrastructure to deliver the planned amount and to do so in a cost-effective way.
While capacity planning and capacity management are sometimes used interchangeably, the two processes are distinctly different. Capacity planning is the determination of how much a company can produce by analyzing the resources available, whereas capacity management is the continuous cycle of monitoring, collecting, and analyzing data, and adjusting infrastructure for optimal output.
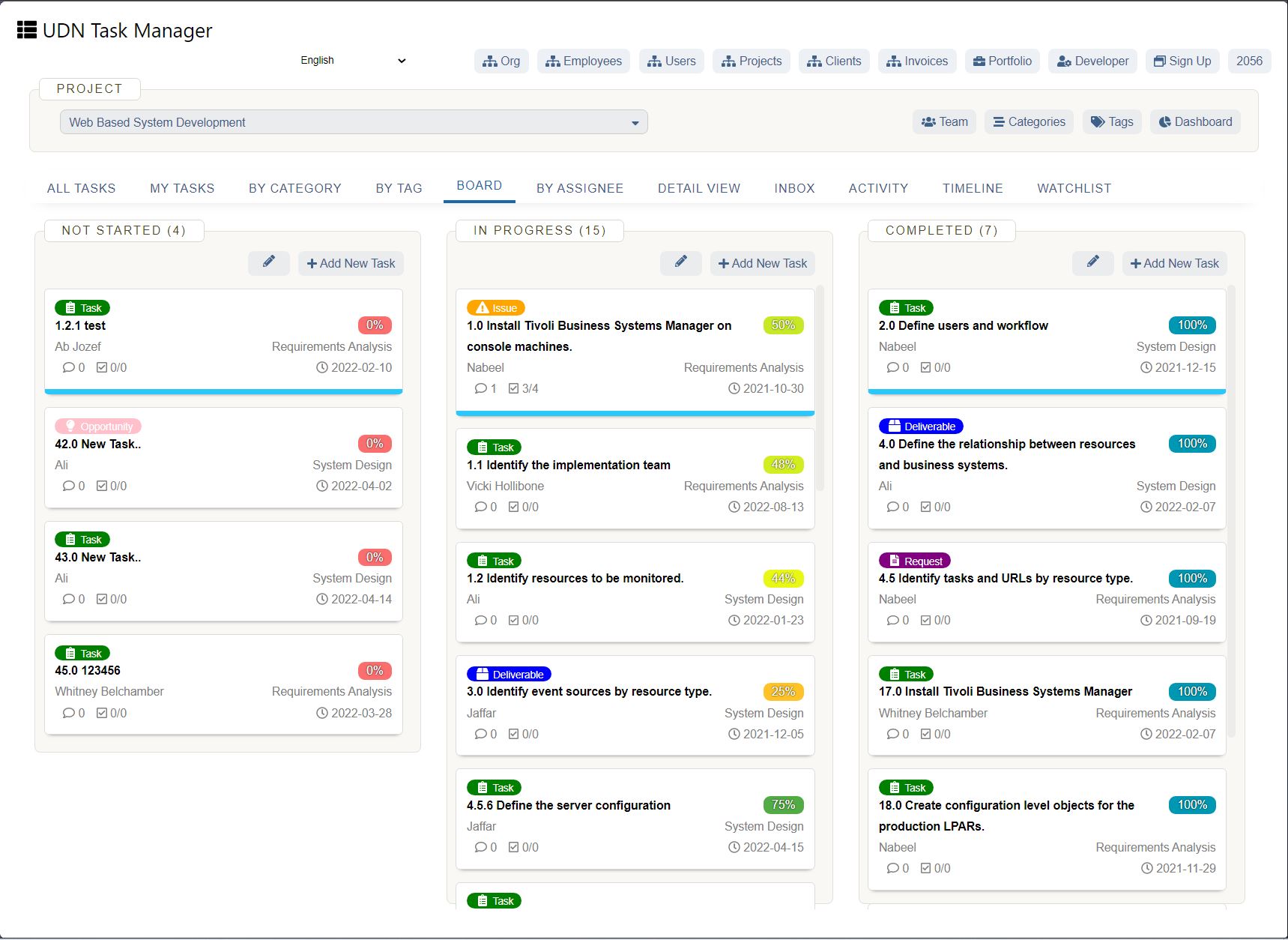
Capacity planning best practices
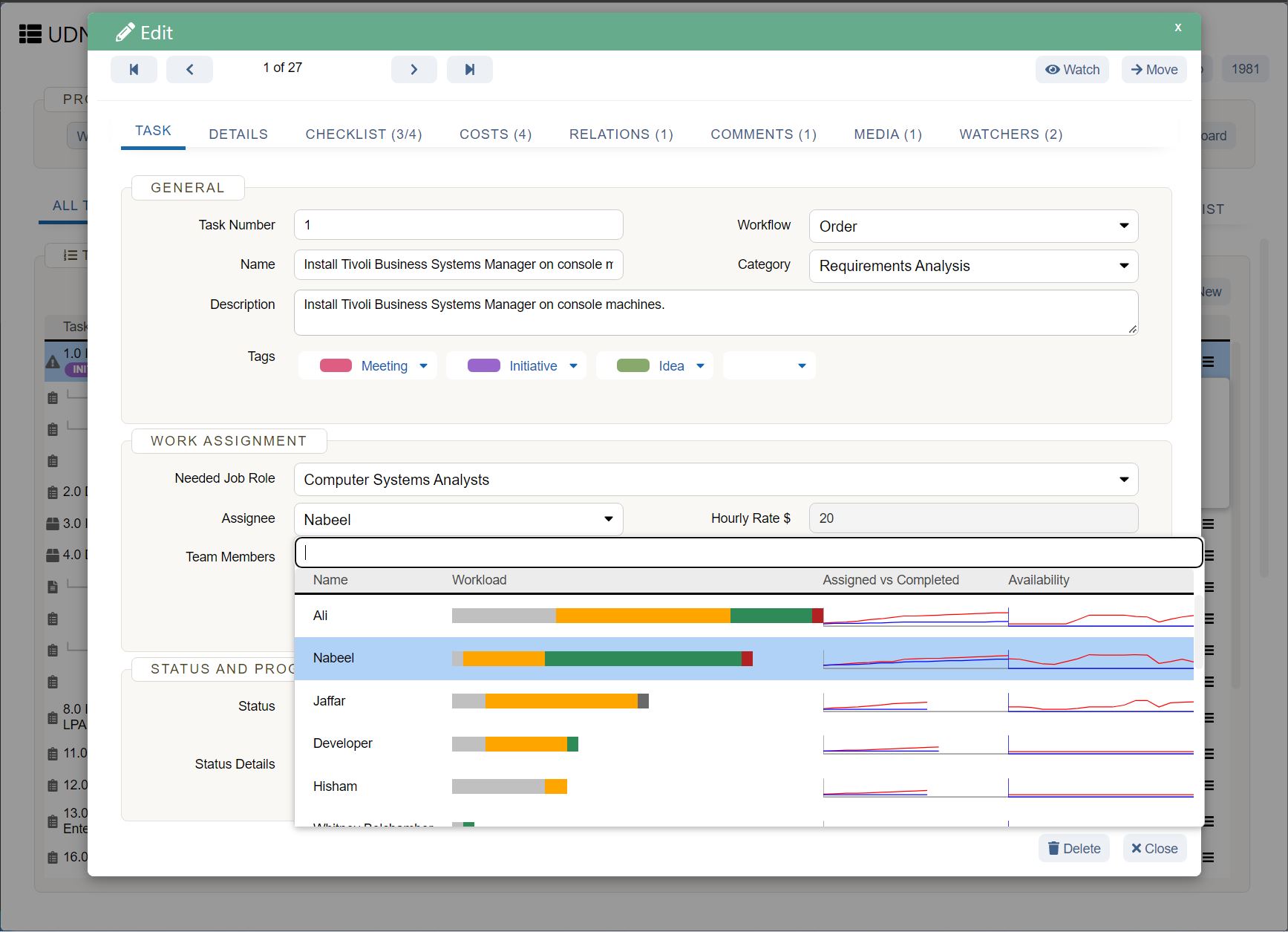
As in any field, capacity planning involves best practices that can help maximize capacity planning efforts. Following these capacity planning best practices can help those involved in project management capacity planning to avoid some of the pitfalls or roadblocks that can impede the process.
Software solutions that provide visibility into individual workloads allow for better capacity planning. UDN Task Manager ’s workload view tool enables resource managers to check short- and long-term availability of individual team members. This is especially useful for teams who work on simultaneous projects.











