10 Top Process Improvement Tools You Need to Create a More Sustainable Business
A study by BCG/MIT finds that 90% of executives deem sustainability to be important, yet only 60% of companies incorporate sustainability as part of their business strategy, and even less (25%) integrate sustainability into the core of their business model.
To generate a clear business case, organizations need to write business operations with sustainability in mind, which can be done by the following two steps:
In this article, you’ll learn how to document your business processes, and why this documentation is important for driving your sustainability agenda. You’ll then be presented with 10 process improvement tools, to help you sow sustainability into the core of your organization.
Why do you need to start thinking about your business processes for corporate sustainability?
At the core of every business are business processes.
A business process is a collection of linked tasks that find their end in the delivery of a service, product, or project.
It’s important to manage your business outputs, aka the product/service/project, but to then supplement this management by process control – especially when it comes to creating a sustainable business, as I’ll explain.
For instance, you might have a sustainability-led project in mind. You can use project management tools and techniques to streamline project planning, resource management , task dependencies, financial planning and manage deliverables. But how do you know operations feeding into a given sustainability project are, also, sustainable?
This is where business processes come into the picture. By documenting your business processes you are separating your end goal, aka the output, from the operations that deliver that output. Keeping these two things separate means you can control business sustainability from all angles.
Before you can make process improvements, you’ll need to document your business processes. Due to the complexity of business operations, use process documentation software, such as a Business Process Management (BPM) platform .
Process documentation gives the transparency needed to improve your business processes.
However, this documentation may seem a daunting task to get started. To help, consider the below steps:
10 Top Process Improvement Tools
Process improvement tools are techniques and methods to be used by organizations that will drive improvements in quality and performance, targeting the processes of a business. In this article, we’re taking a unique look at these tools with sustainability in mind. That is, what are the top process improvement tools that can deliver sustainability improvements within an organization?
Gap analysis examines and assesses performance to identify the difference between your current business state and where you’d like to be. To complete a gap analysis, you’ll need to define:
As a means of evaluating current sustainability performance, follow pre-established best practices – aka sustainability standards – to evaluate your current sustainability performance. Popular global standards to follow include:
Once a current performance measure has been determined, you can define your ideal situation based on meeting or surpassing standard requirements.
Next lay out a clear framework that will take you from your current performance to your ideal situation, potential. To do this, define:
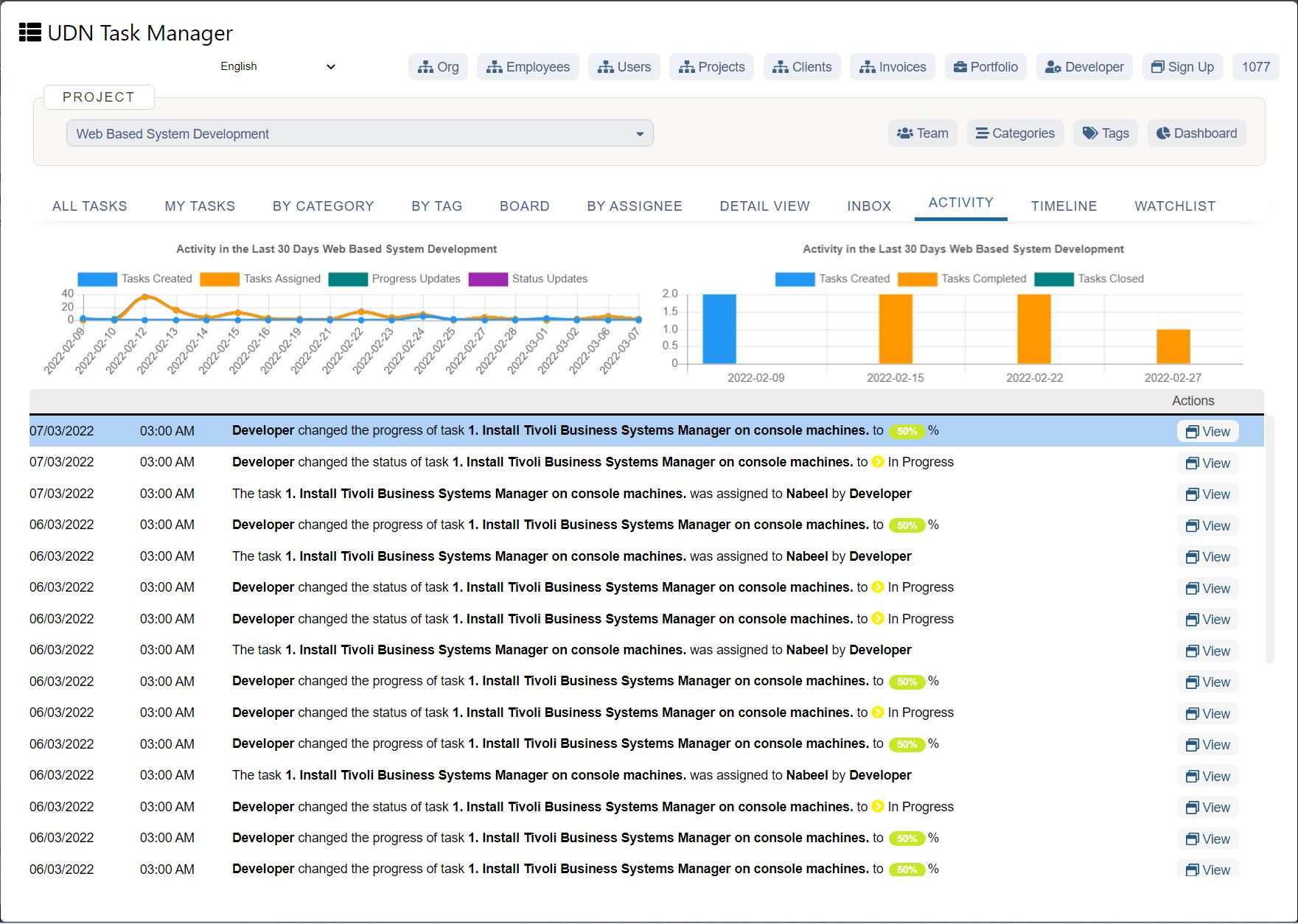
Root cause analysis helps you understand the causal focus underlying the issues behind your biggest business sustainability pain points.
This is a great process improvement tool to use alongside gap analysis. I.e. What’s preventing you from reaching your potential state?
Root Cause Analysis acknowledges root cause issues as not-so-obvious problems. A common method to implement Root Cause Analysis is via the Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa diagram) – as presented below.
To produce a fishbone diagram, complete the following steps:
Hoshin Kanri is a strategic planning method ensuring everyone in an organization is driving towards the same goals. The method moves away from the typical top-down deployment of organizational change , towards a bottom-up approach.
That is, everyone in the organization is involved in setting improvement priorities. The method takes improvement objectives – e.g. this could be your objectives set to solve a given root cause – and then breaks these objectives down into smaller objectives, which are broken down further into projects. Projects are distributed around your team.
The Hoshin Kanri methodology creates and maintains transparent feedback loops across all hierarchical levels in an organization. The idea is to maintain an open two-way stream for information sharing.
Source
Your sustainability objectives are passed, like a ball, from top-level management to lower organizational levels. Lower levels then relay feedback and tactic propositions back to upper management. There may be a few iterative ball-passing until a consensus is reached and your sustainability objective is obtained.
You can use gap analysis to define where you want to be operating ( your potential ), then define the root cause using root cause analysis, set your objectives, and effectively install sustainable change using the Hoshin Kanri methodology.

The PDCA cycle stands for P lan, D o, C heck and A ct . It’s a process improvement tool detailing 4 steps for implementing sustainability improvements, as follows:
The PDCA cycle centers around the idea that more can always be done . The concept is a cycle, meaning organizations will continuously assess where they lie on the sustainability agenda and act/make process changes accordingly.
With only ⅔’s of U.S. citizens concerned about climate change, not everyone in your team will be fully engaged and on your side when sustainability-related changes are introduced.
For this reason, you’ll need an effective change management technique in your process improvement toolbox. Here we take a look at Lewin’s Force Field Model .
Lewin’s model gives a problem overview and splits factors into forces for (driving forces) and against (restraining forces) organizational change. When these forces are balanced, there’s no change. To introduce organizational change, driving forces need to be boosted and restraining forces need to be alleviated. To accomplish this, the model splits the process of implementing change into 3 stages:
Just In Time production is a management philosophy used to control production processes. It’s about producing what the customer wants, when they want it, in the quantities requested, where they want it, and without delays.
JIT is pull-system meaning investments are governed by process demand. This demand-pull means an organization only gives what’s necessary to obtain the required output in a business system.
The JIT framework keeps stock levels of raw materials, components, work in progress, and finished goods to a minimum. This reduces waste and natural resource use, helping organizations operate more sustainably.
JIT isn’t an overly complicated system, but making it work effectively requires careful planning and lots of preparation. To implement JIT, you’ll have to consider the following:
Lean Six Sigma gives a structured approach to scrutinize operations, looking at data and processes to uncover and remove waste.
You can implement the lean Six Sigma process improvement tool through the 5-stepped model, DMAIC, as follows:
Using the DMAIC methodology will deliver continuous improvements, to help you establish greener business operations.
SIPOC is an acronym for S uppliers, I nputs, P rocesses, O utputs, and C ustomers.
The methodology acts as a tool to identify the inputs and outputs of target business processes, to determine the process owner, customers, suppliers, and to establish clear boundaries for the process.
Use the SIPOC methodology during the measure phase of DMAIC, to analyze different processes in a working system. The SIPOC methodology gives an overall system perspective by answering the following questions:
With this information, you can easily identify sustainability problems or weaknesses.
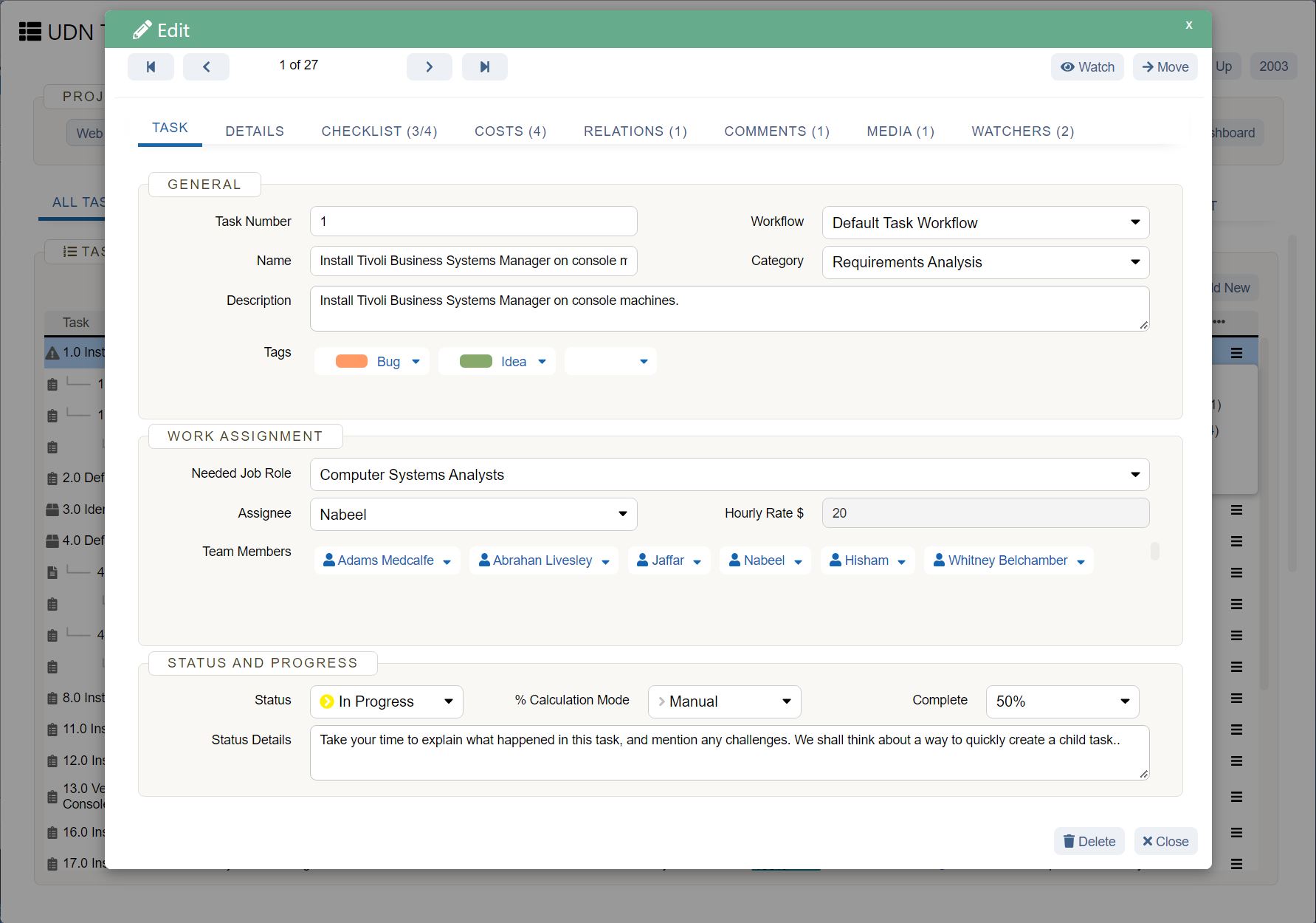
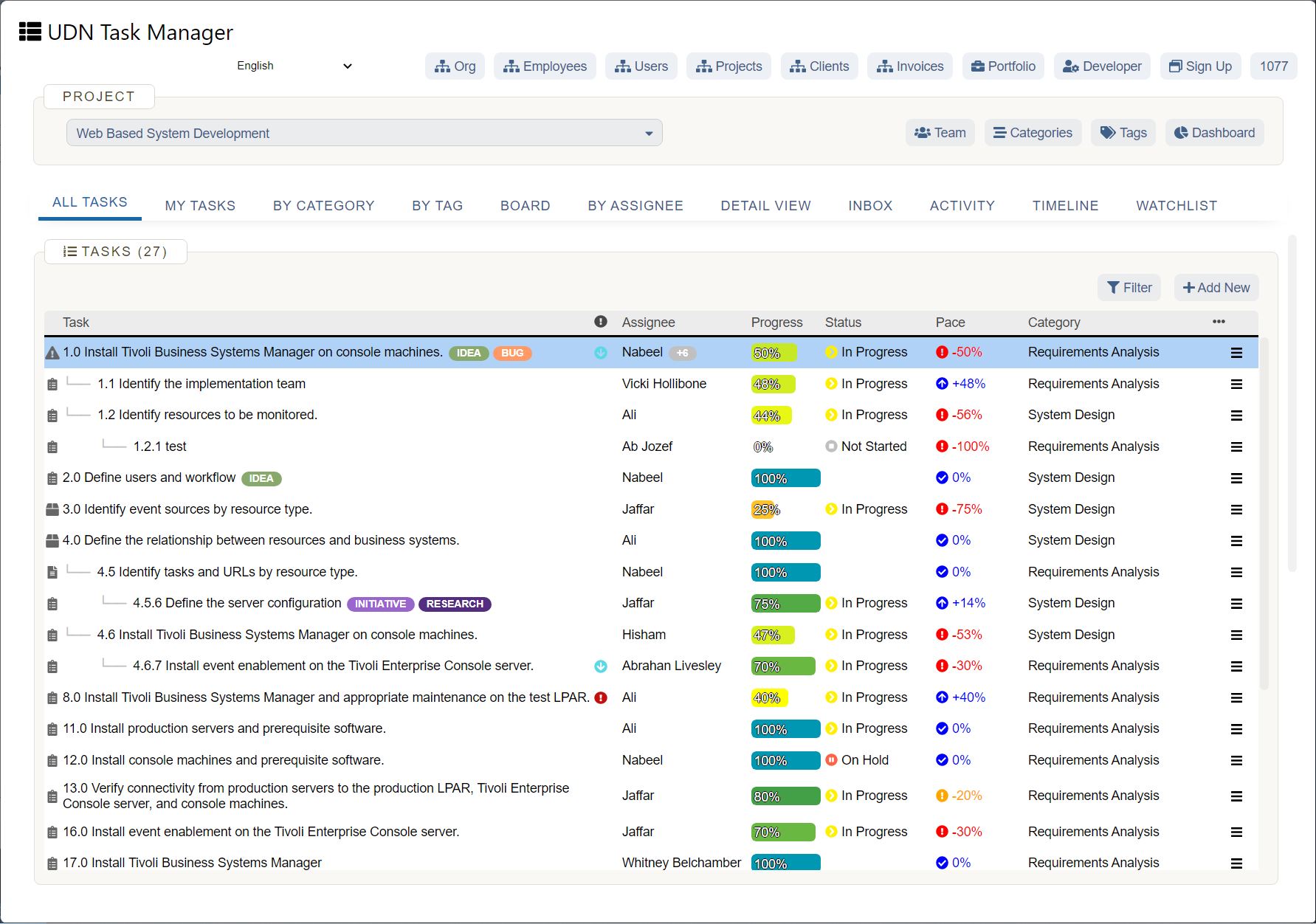
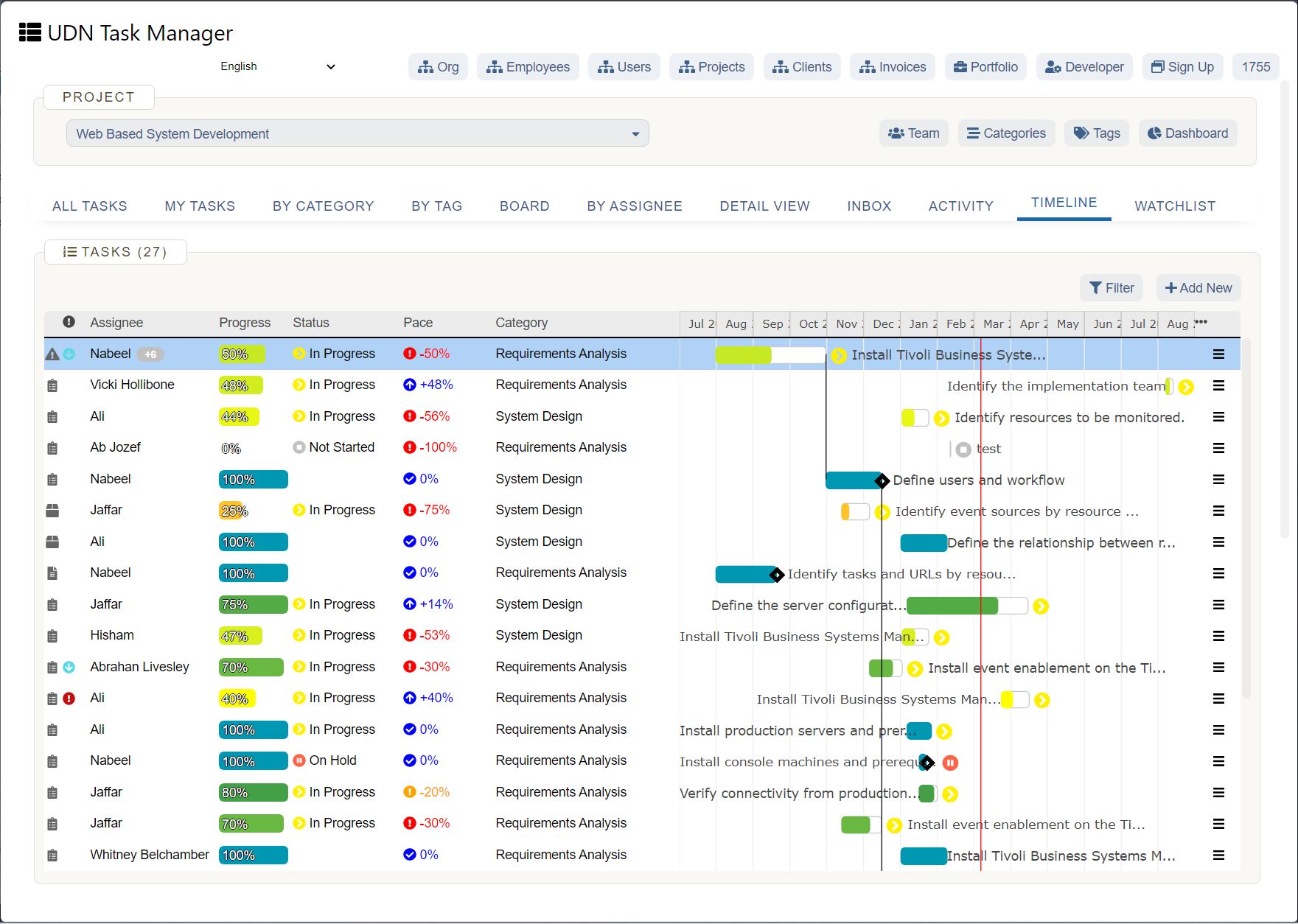
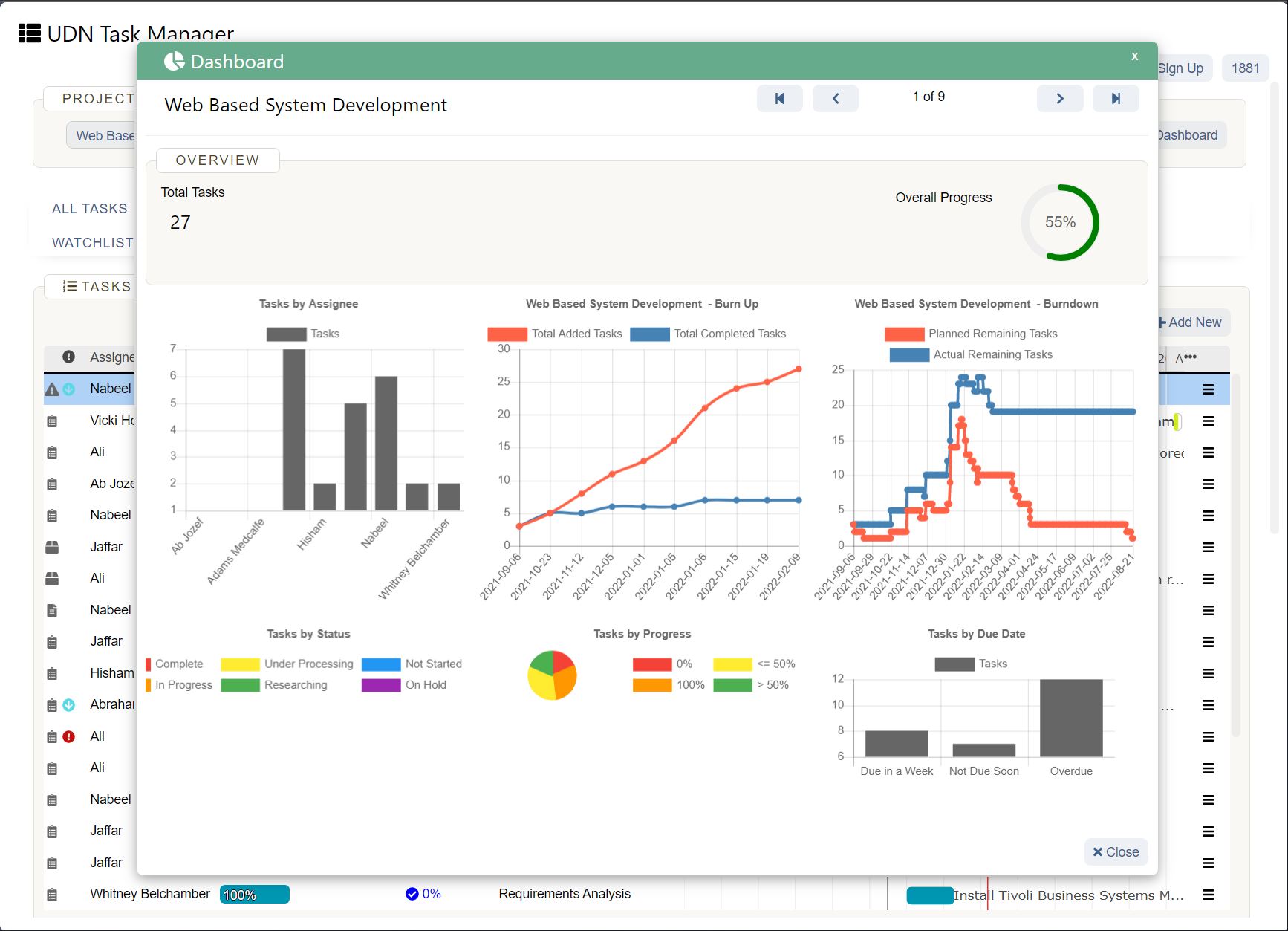
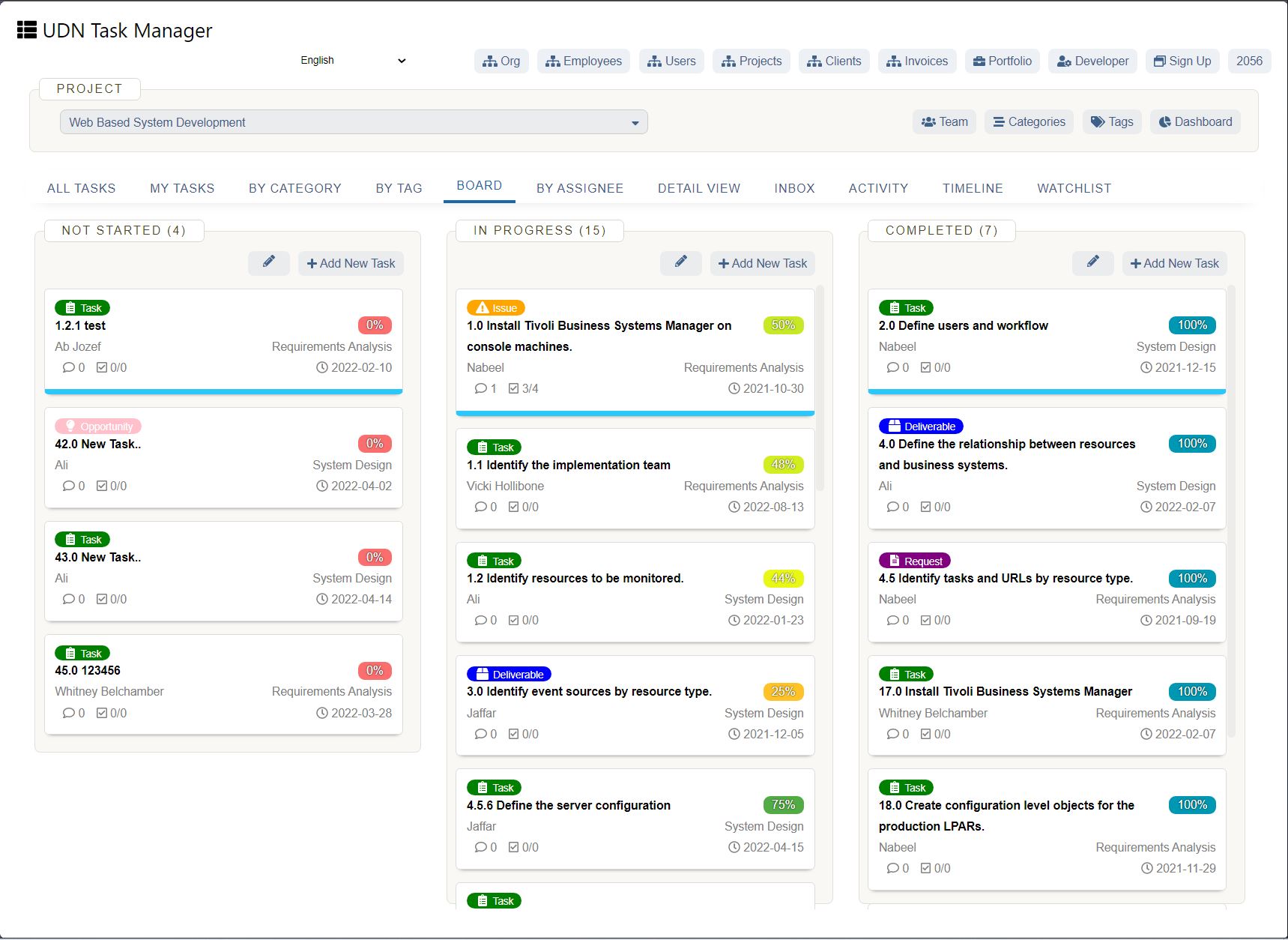
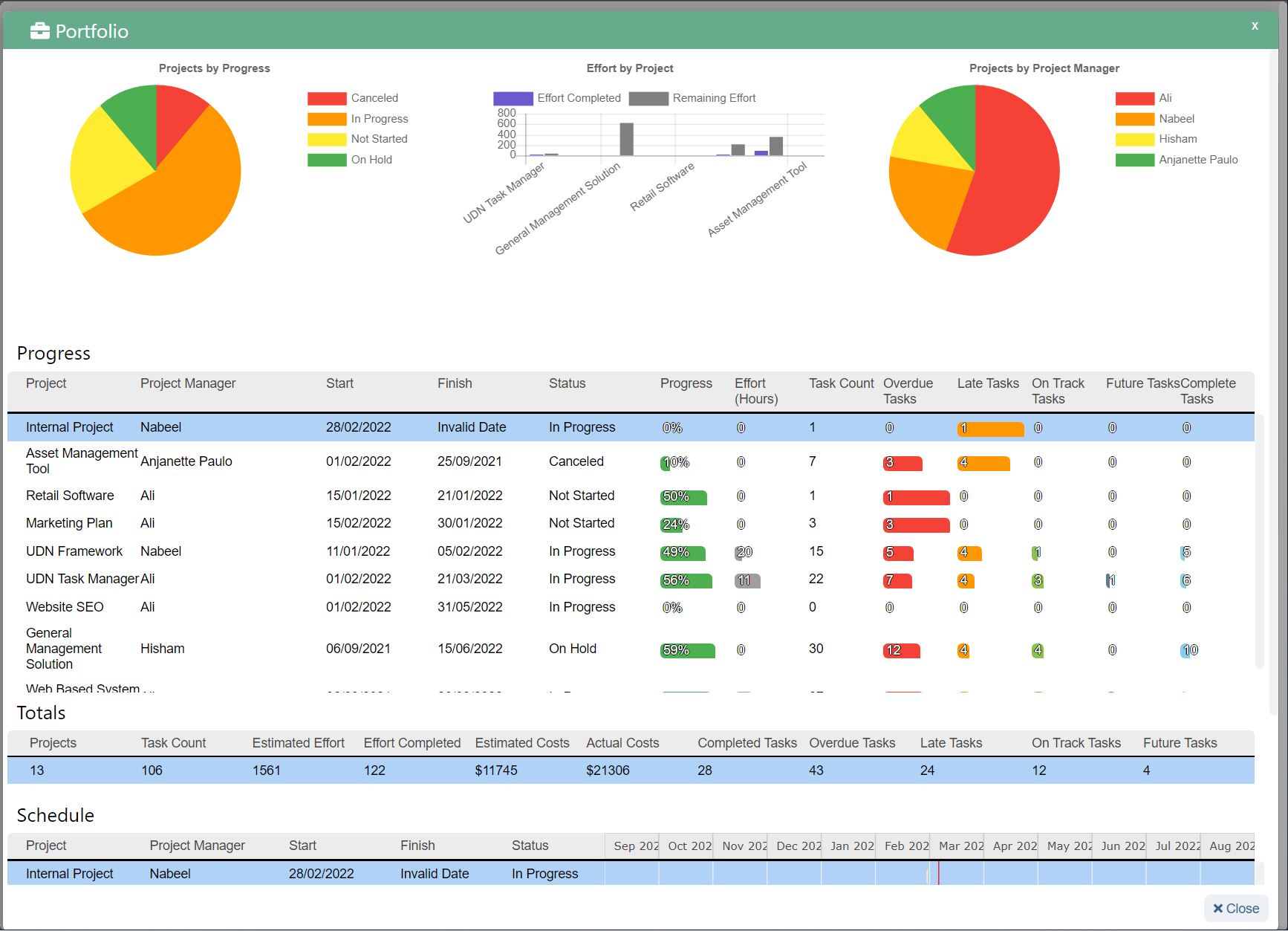
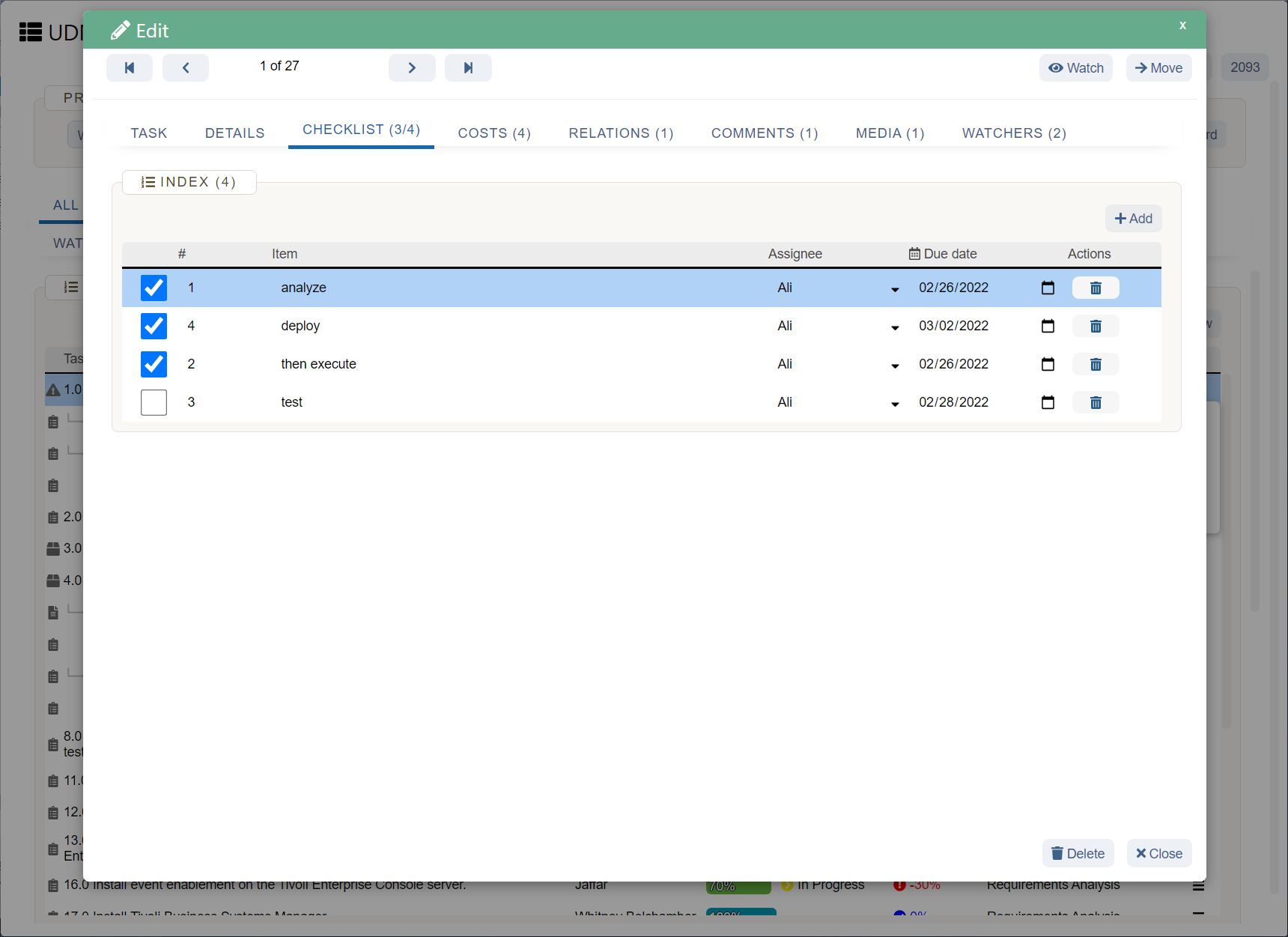
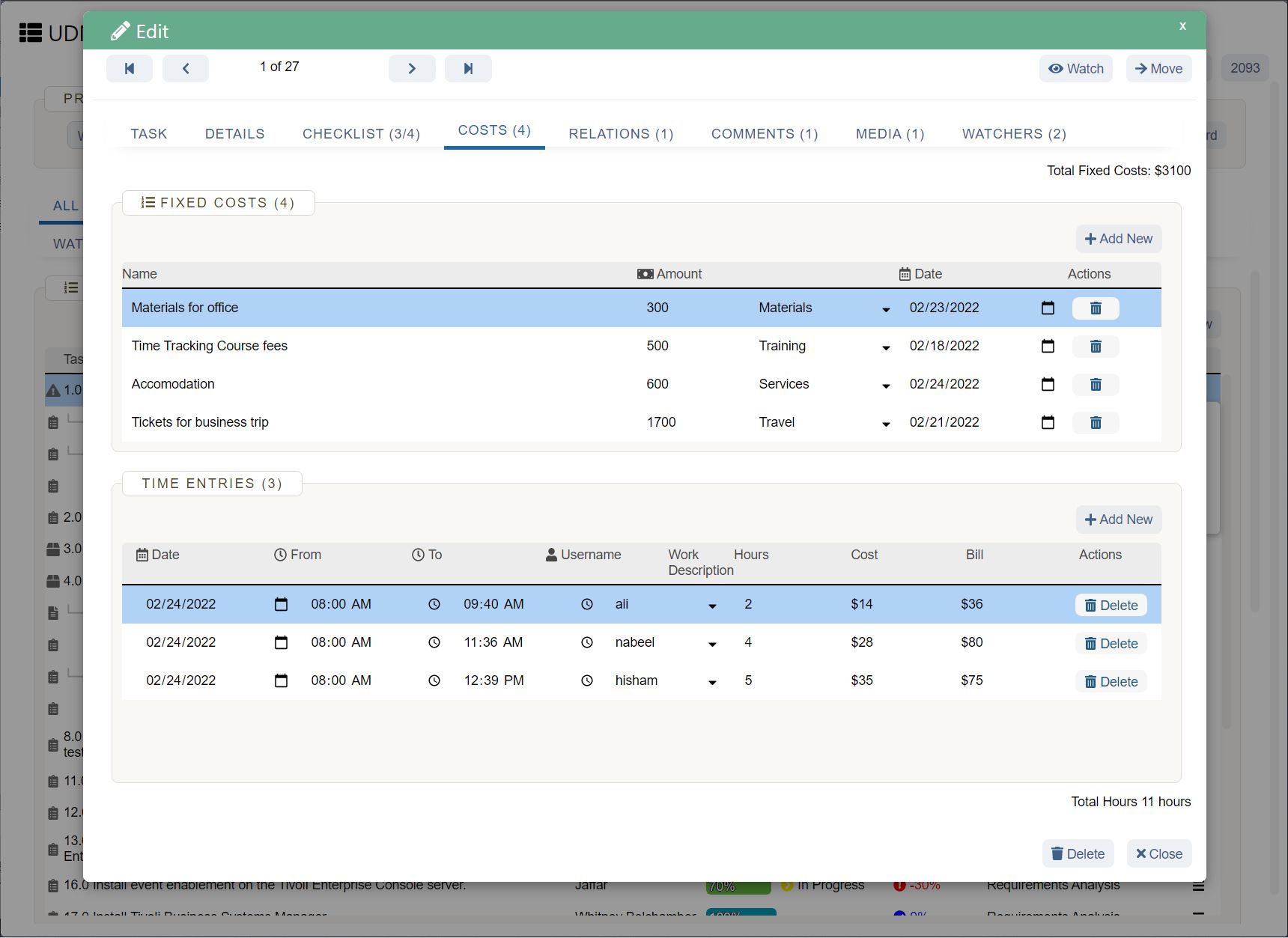
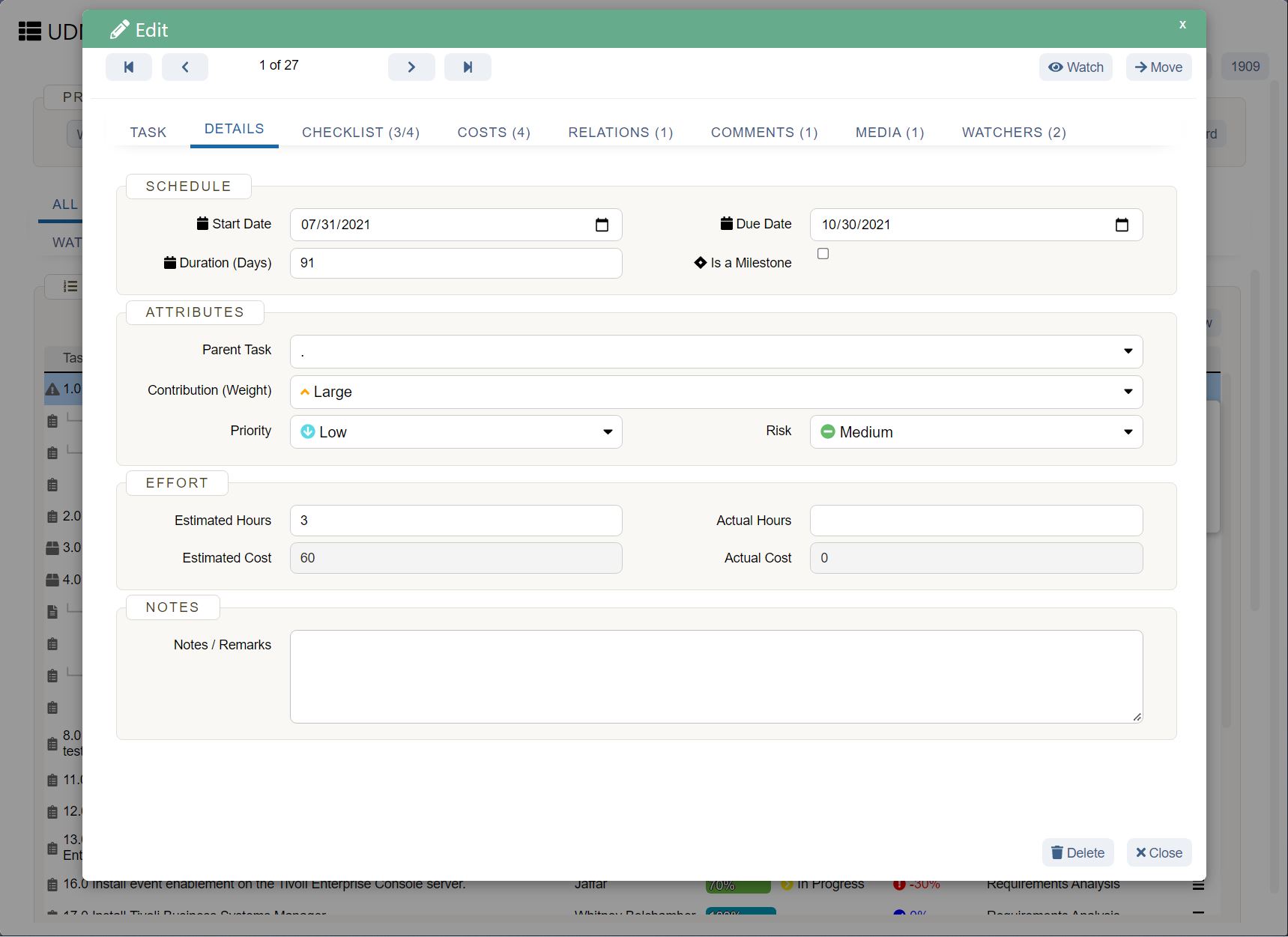
UDN Task Manager Kanban Boards
Kanban is a work management system used to identify where work gets stuck or blocked. It’s a lean methodology used to communicate what, when and how much of something is needed to be produced via using Kanban boards and task cards.
Kanban is an effective method to drive efficiency improvements in a business and reduce waste – when thinking about resource use, you can see how the implementation of Kanban can improve business sustainability.
There a 5 main steps to implementing Kanban, which include:
Prioritization matrix analysis is a task analysis method used to identify and depict relationships between concepts.
Sustainability-related issues are complex and are defined as wicked problems . Wicked in the sense that the issues are interconnected, have many feedback loops – meaning improvements in one area can degrade another area – and require cross-sector collaboration. Deciphering the appropriate business resolutions can therefore feel overwhelming – where do you start?
The prioritization matrix helps you order your priorities, grouping process solutions into four separate categories of importance.
To complete a prioritization matrix, follow the below steps:
Improving the sustainability of your business operations should be considered a continuous process . You can use the process improvement tools given in this article to help you write sustainability into the core of your business model.
Follow: @JaneCourtnell











