Create a sales forecast template in 5 simple steps (with examples)
Summary
A sales forecast predicts future sales revenue using past business data. You can use sales forecasting to assess your financial projections and change your business plan if necessary. Learn how a sales forecast template can help you set goals, budget, and refine your sales cycle.
A strong sales team is the key to success for most companies. They say a good salesperson can sell sand at the beach, but whether you’re selling products in the Caribbean or Antarctica, it all comes down to strategy. When you’re unsure if your current strategy is working, a sales forecast can help.
A sales forecast projects future business revenue based on historical data. You can use sales forecasting to preview your financial projections. Based on how promising those projections are, you can make tweaks and adjustments to your business plan if necessary. In this article, we cover how to create a sales forecast template, which you can use to improve future performance.
What is a sales forecast?
A sales forecast predicts future sales revenue using past business data. Your sales forecast can also predict the total number of units you might sell on a new product, the customers you’ll gain, or the memberships you’ll sell in a given time period..
Once you calculate your sales projections, you can use the results to assess your business health and adjust your plans accordingly.
How to create a sales forecast template
There are different sales forecasting methods, and some are simpler than others. With the steps below, you’ll have a basic understanding of how to create a sales forecast template that you can customize to the method of your choice.
1. Track your business data
Without details from your past sales, you won’t have anything to base your predictions on. If you don’t have past sales data, you can begin tracking sales now to create a sales forecast in the future. The data you’ll need to track includes:
Number of units sold per month
Revenue of each product by month
Number of units returned or canceled (so you can get an accurate sales calculation)
Other items you can track to make your predictions more accurate include:
Growth percentage
Number of sales representatives
Average sales cycle length
There are different ways to use these data points when forecasting sales. If you want to calculate your sales run rate, which is your projected revenue for the next year, use your revenue from the past month and multiply it by 12. Then, adjust this number based on other relevant data points, like seasonality.
Tip: The best way to track historical data is to use customer relationship management (CRM) software. When you have a CRM strategy in place, you can easily pull data into your sales forecast template and make quick projections.
2. Set your metrics
Before you perform the calculations in your sales forecast template, you need to decide what you’re measuring. The basic questions you should ask are:
What is the product or service you’re selling and forecasting for? Answering this question helps you decide what exactly you’re evaluating. For example, you can investigate future trends for a long-standing product to decide whether it’s worth continuing, or you can predict future sales for a new product.
How far in the future do you want to make projections? You can decide to make projections for as little as six months or as much as five years in the future. The complexity of your sales forecast is up to you.
How much will you sell each product for , and how do you measure your products? Set your product’s metrics, whether they be units, hours, memberships, or something else. That way, you can calculate revenue on a price per unit basis.
How long is your sales cycle? Your sales cycle—also called a sales funnel—is how long it takes for you to make the average sale from beginning to end. Sales cycles are often monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Depending on the product you’re selling, your sales cycle may be unique. Steps in the sales cycle typically include:
Lead generation
Lead qualification
Initial contact
Making an offer
Negotiation
Closing the deal
Tip: You can still project customer growth versus revenue even if your company is in its early phases. If you don’t have enough historical data to use for your sales forecast template, you can use data from a company similar to yours in the market.
3. Choose a forecasting method
There are two basic forecasting methods you can use when sales forecasting. The top-down method starts with the total size of the market and works down, while the bottom-up method starts with your business and expands out.
Top-down method: To use the top-down method, start with the total size of the market—or total addressable market (TAM). Then, estimate how much of the market you think your business can capture. For example, if you’re in a large, over-saturated market, you may only capture 3% of the TAM. If the total addressable market is $1 billion, your projected annual sales would be $30 million.
Bottom-up method: With the bottom-up method, you’ll estimate the total units your company will sell in a sales cycle, then multiply that number by your average cost per unit. You can expand out by adding other variables, like the number of sales reps, department expenses, or website views. The bottom-up forecasting method uses company data to project more specific results.
You’ll need to choose one method to fill in your sales forecast template, but you can also try both methods to compare results.
Tip: The best forecasting method for you may depend on what type of business you’re running. If your company experiences little fluctuation in revenue, then the top-down forecasting method should work well. The top-down model can also work for new businesses that have little business data to work with. Bottom-up forecasting may be better for seasonal businesses or startups looking to make future budget and staffing decisions.
4. Calculate your sales forecast
You’ve already learned a basic way to calculate revenue using the top-down method. Below, you’ll see another way to estimate your projected sales revenue on an annual scale.
Divide your sales revenue for the year so far by the number of months so far to calculate your average monthly sales rate.
Multiply your average monthly sales rate by the number of months left in the year to calculate your projected sales revenue for the rest of the year.
Add your total sales revenue so far to your projected sales revenue for the rest of the year to calculate your annual sales forecast.
A more generalized way to estimate your future sales revenue for the year is to multiply your total sales revenue from the previous year.
Example: Let’s say your company sells a software application for $300 per unit and you sold 500 units from January to March. Your sales revenue so far is $150,000 ($300 per unit x 500 units sold). You’re three months into the calendar year, so your average monthly sales rate is $50,000 ($150,000 / 3 months). That means your projected sales revenue for the rest of the year is $450,000 ($50,000 x 9 months).
5. Adjust for external factors

A sales forecast predicts future revenue by making assumptions about your growth rate based on past success. But your past success is only one component of your growth rate. There are external factors outside of your control that can affect sales growth—and you should consider them if you want to make accurate projections.
Some external factors you can adjust your calculations around include:
Inflation rate: Inflation is how much prices increase over a specific time period, and it usually fluctuates based on a country’s overall economic state. You can take your annual sales forecast and factor in inflation rate to ensure you’re not projecting a higher or lower number of sales than the economy will permit.
The competition: Is your market becoming more competitive as time goes on? For example, are you selling software during a tech boom? If so, assess whether your market share will shrink because of rising competition in the coming year(s).
Market changes: The market can shift as people change their behavior. Your audience may spend an average of six hours per day on their phones in one year. In the next year, mental health awareness may cause phone usage to drop. These changes are hard to predict, so you must stay on top of market news.
Industry changes: Industry changes happen when new products and technologies come on the market and make other products obsolete. One instance of this is the invention of AI technology.
Legislation: Although not as common, changes in legislation can affect the way companies sell their products. For example, vaping was a multi-million dollar industry until laws banned the sale of vape products to people under the age of 21.
Seasonality: Many industries experience seasonality based on how human behavior and human needs change with the seasons. For example, people spend more time inside during the winter, so they may be on their computers more. Retail stores may also experience a jump in sales around Christmas time.
Tip: You can create a comprehensive sales plan to set goals for team members. Aside from revenue targets and training milestones, consider assigning each of these external factors to your team members so they can keep track of essential information. That way, you’ll have your bases covered on anything that may affect future sales growth.
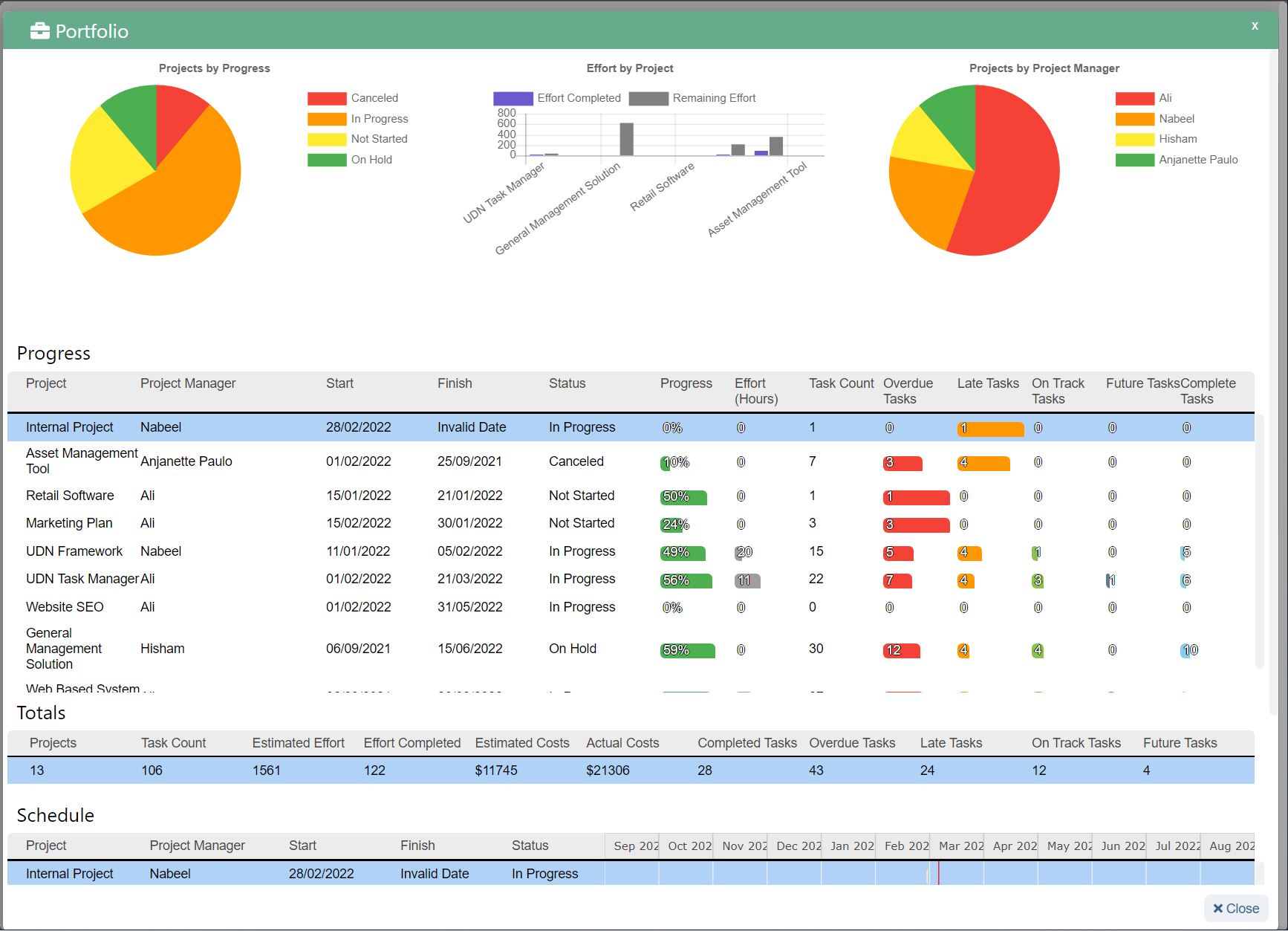
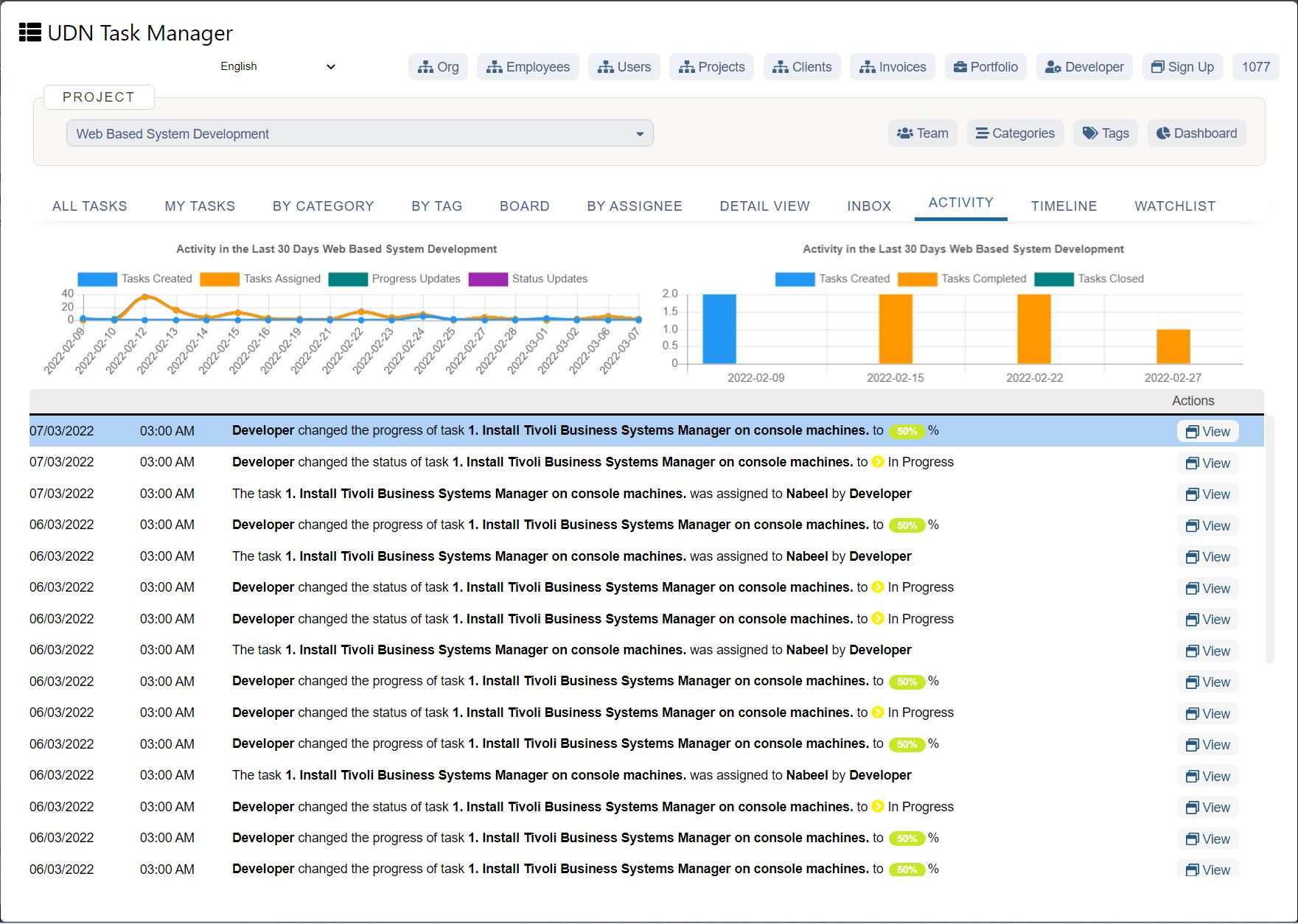
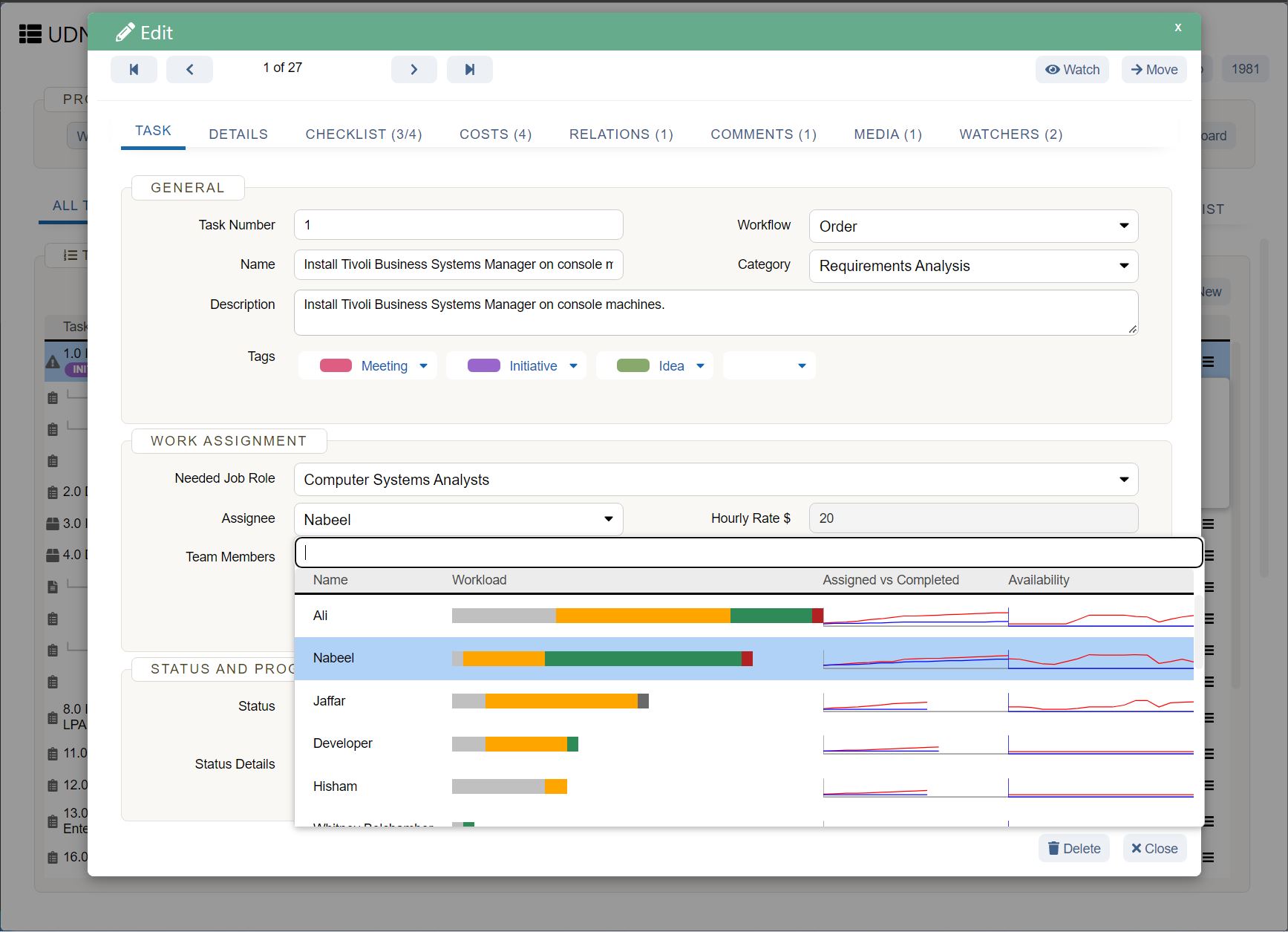
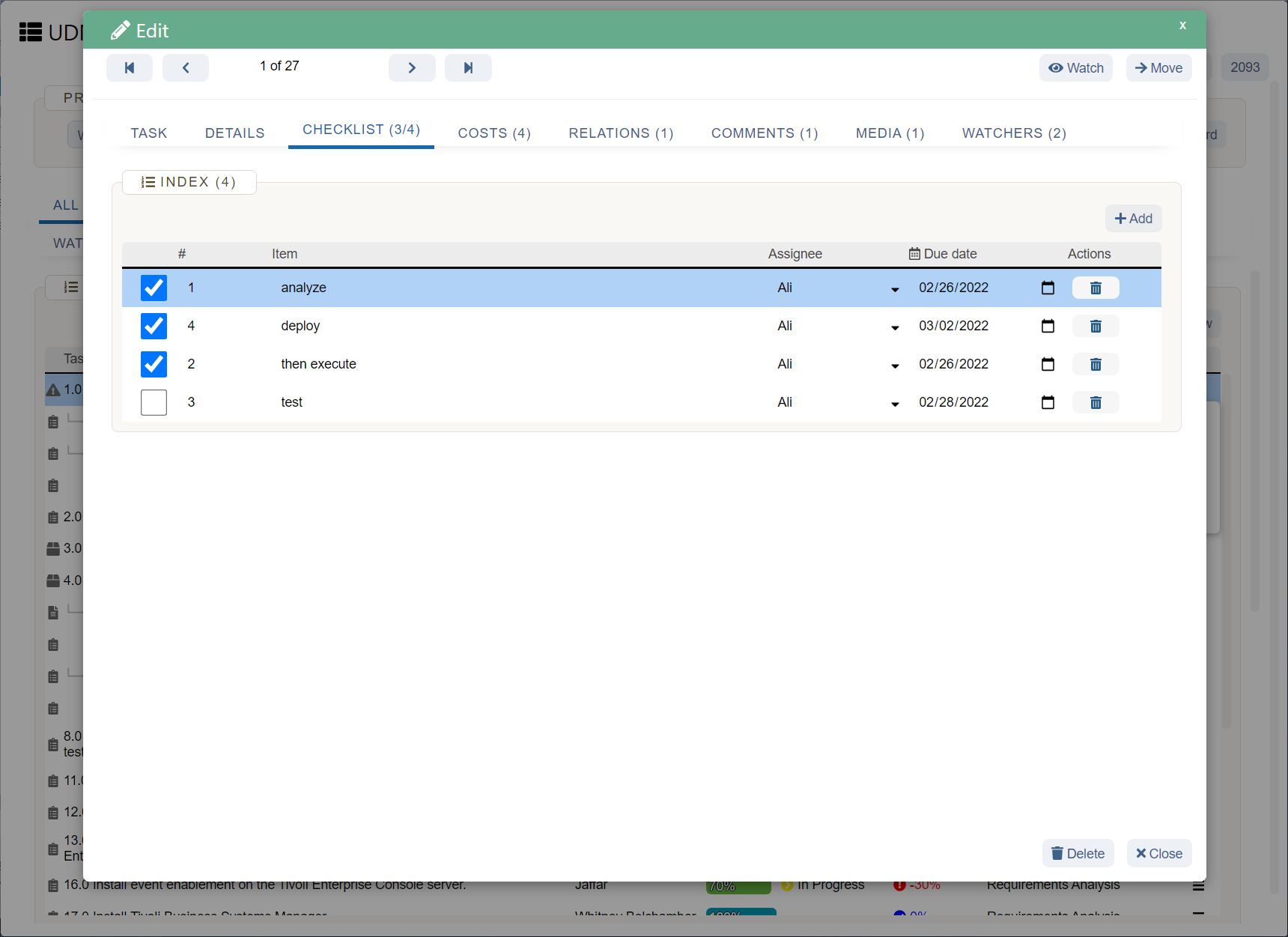
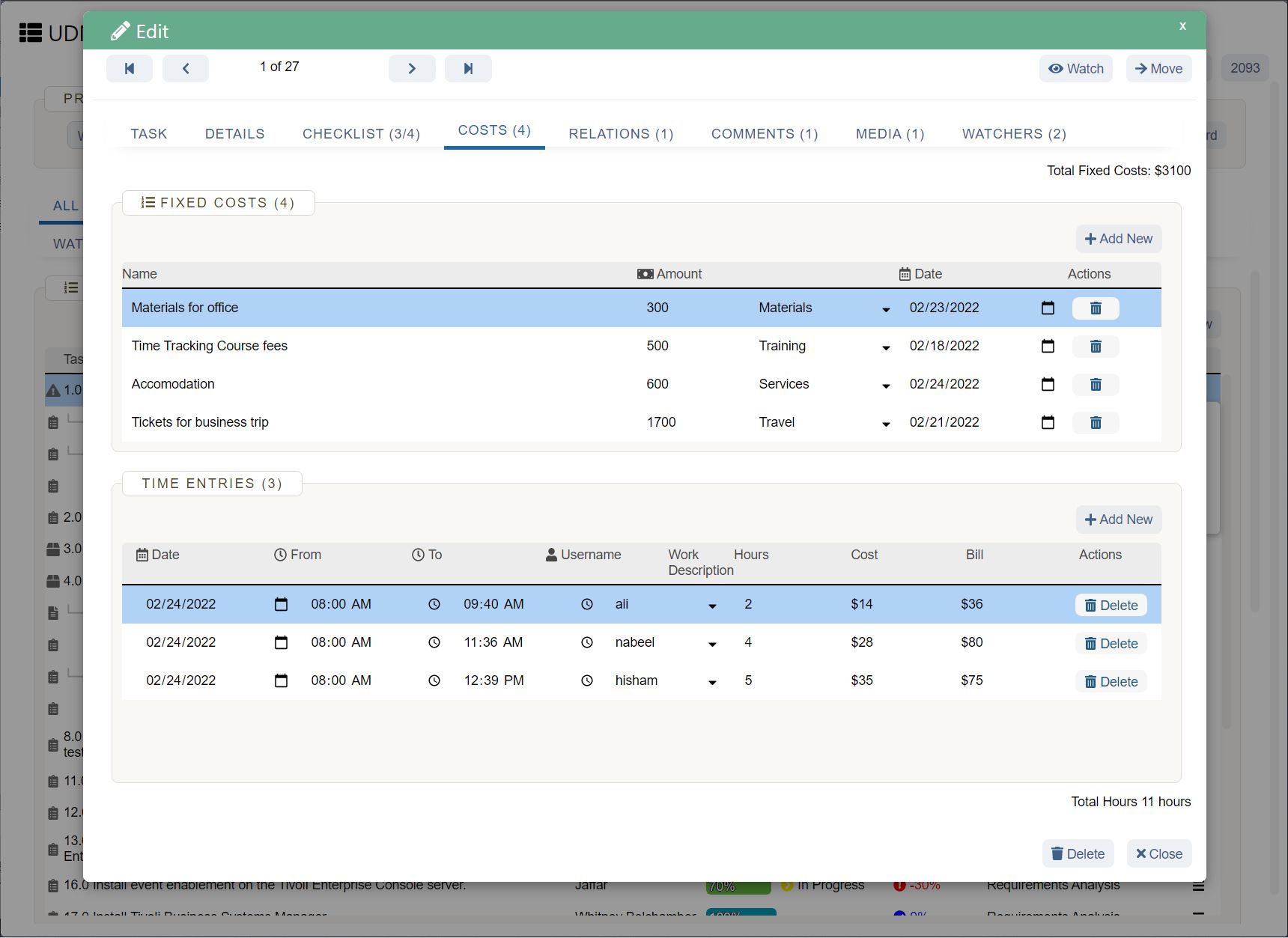
Sales forecast template (and example)
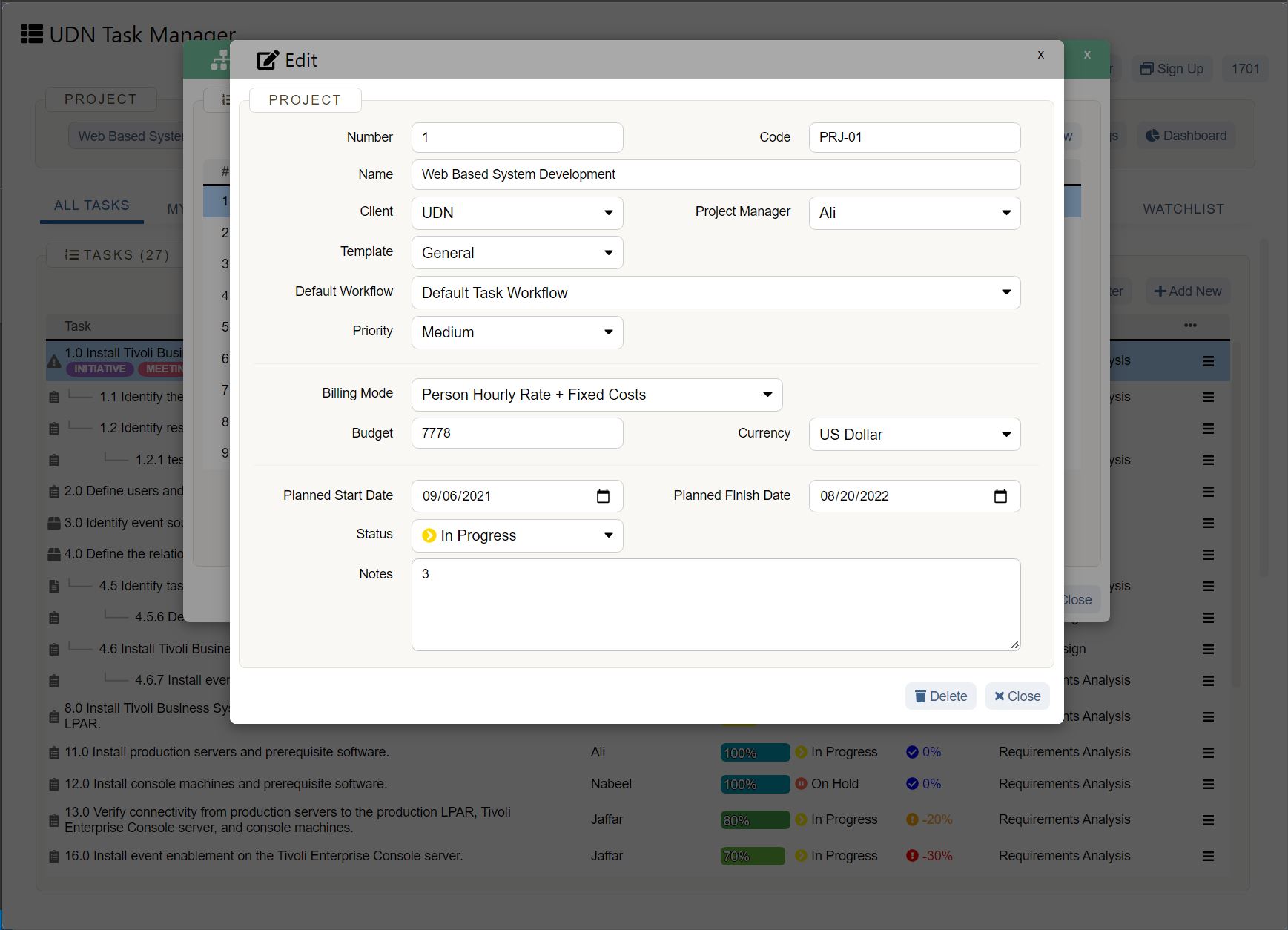
Below you’ll see an example of a software company’s six-month sales forecast template for two products. Product one is a software application, and product two is a software accessory.
In this sales forecast template, the company used past sales data to fill in each month. They projected their sales would increase by 10% each month because of a 5% increase in inflation and because they gained 5% more of the market. They kept their price per unit the same as the previous year.
Putting both products in the same chart can help the company see that their lower-cost product—the software accessory—brings in more revenue than their higher-cost product. The company can then use this insight to create more low-cost products in the future.
Download the free sales forecast template below to assess your future sales performance.
Why is sales forecasting important?
Sales forecasting is an important tool used to monitor business health.
An effective sales forecasting plan:
Predicts demand: When you have an idea of how many units you may sell, you can get a head start on production.
Helps you make smart investments: If you have future goals of expanding your business with new locations or products, knowing when you’ll have the income to do so is important.
Contributes to goal setting: Your sales forecast can help you set goals outside of investments as well, like outshining competitors or hiring new team members.
Guides spending: Your sales forecast may be the wake-up call you need to set a budget and use cost control to reduce expenses.
Improves the sales process: You can change your current sales process based on the sales projections you’re unhappy with.
Highlights financial problems: Your sales forecast template will open your eyes to problem areas you may not have noticed otherwise.
When you have an accurate prediction of your future sales, you can use your projections to adjust your current sales process.
Pair your sales forecast with a strong sales process
A sales forecast is only one part of the larger sales picture. This tool gives you a view into the future, but you’ll need to take action to see results. Sales management software can help you organize tasks, set up projects, and engage customers.
As your team members acquire leads and close deals, you can track them through the sales pipeline. A solid sales plan is the foundation of future success.











